Pathogenesis of permeability barrier abnormalities in the ichthyoses: inherited disorders of lipid metabolism
- PMID: 18245815
- PMCID: PMC2844331
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R800002-JLR200
Pathogenesis of permeability barrier abnormalities in the ichthyoses: inherited disorders of lipid metabolism
Abstract
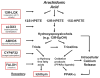
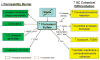
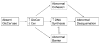
Many of the ichthyoses are associated with inherited disorders of lipid metabolism. These disorders have provided unique models to dissect physiologic processes in normal epidermis and the pathophysiology of more common scaling conditions. In most of these disorders, a permeability barrier abnormality "drives" pathophysiology through stimulation of epidermal hyperplasia. Among primary abnormalities of nonpolar lipid metabolism, triglyceride accumulation in neutral lipid storage disease as a result of a lipase mutation provokes a barrier abnormality via lamellar/nonlamellar phase separation within the extracellular matrix of the stratum corneum (SC). Similar mechanisms account for the barrier abnormalities (and subsequent ichthyosis) in inherited disorders of polar lipid metabolism. For example, in recessive X-linked ichthyosis (RXLI), cholesterol sulfate (CSO(4)) accumulation also produces a permeability barrier defect through lamellar/nonlamellar phase separation. However, in RXLI, the desquamation abnormality is in part attributable to the plurifunctional roles of CSO(4) as a regulator of both epidermal differentiation and corneodesmosome degradation. Phase separation also occurs in type II Gaucher disease (GD; from accumulation of glucosylceramides as a result of to beta-glucocerebrosidase deficiency). Finally, failure to assemble both lipids and desquamatory enzymes into nascent epidermal lamellar bodies (LBs) accounts for both the permeability barrier and desquamation abnormalities in Harlequin ichthyosis (HI). The barrier abnormality provokes the clinical phenotype in these disorders not only by stimulating epidermal proliferation, but also by inducing inflammation.
Figures
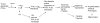


References
-
- Feingold KR. The regulation and role of epidermal lipid synthesis. Adv Lipid Res. 1991;24:57–82. - PubMed
-
- Elias PM, Crumrine D, Rassner U, Hachem JP, Menon GK, Man W, Choy MH, Leypoldt L, Feingold KR, Williams ML. Basis for abnormal desquamation and permeability barrier dysfunction in RXLI. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;122:314–319. - PubMed
-
- Holleran WM, Ziegler SG, Goker-Alpan O, Eblan MJ, Elias PM, Schiffmann R, Sidransky E. Skin abnormalities as an early predictor of neurologic outcome in Gaucher disease. Clin Genet. 2006;69:355–357. - PubMed
-
- Schmuth M, Man MQ, Weber F, Gao W, Feingold KR, Fritsch P, Elias PM, Holleran WM. Permeability barrier disorder in Niemann-Pick disease: sphingomyelin-ceramide processing required for normal barrier homeostasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:459–466. - PubMed
-
- Williams ML. Ichthyosis: mechanisms of disease. Pediatr Dermatol. 1992;9:365–368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

