Evidence of spatially varying selection acting on four chromatin-remodeling loci in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 18245821
- PMCID: PMC2390624
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.085423
Evidence of spatially varying selection acting on four chromatin-remodeling loci in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
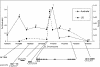
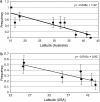
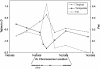
The packaging of DNA into proper chromatin structure contributes to transcriptional regulation. This packaging is environment sensitive, yet its role in adaptation to novel environmental conditions is completely unknown. We set out to identify candidate chromatin-remodeling loci that are differentiated between tropical and temperate populations in Drosophila melanogaster, an ancestrally equatorial African species that has recently colonized temperate environments around the world. Here we describe sequence variation at seven such chromatin-remodeling loci, four of which (chd1, ssrp, chm, and glu) exhibit strong differentiation between tropical and temperate populations. An in-depth analysis of chm revealed sequence differentiation restricted to a small portion of the gene, as well as evidence of clinal variation along the east coasts of both the United States and Australia. The functions of chd1, chm, ssrp, and glu point to several novel hypotheses for the role of chromatin-based transcriptional regulation in adaptation to a novel environment. Specifically, both stress-induced transcription and developmental homeostasis emerge as potential functional targets of environment-dependent selection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genomic analysis of adaptive differentiation in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2008 May;179(1):455-73. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.083659. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18493064 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary inferences from DNA variation at the 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase locus in natural populations of drosophila: selection and geographic differentiation.Genetics. 1994 Jan;136(1):155-71. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.1.155. Genetics. 1994. PMID: 8138153 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide patterns of latitudinal differentiation among populations of Drosophila melanogaster from North America.Mol Ecol. 2012 Oct;21(19):4748-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05731.x. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Mol Ecol. 2012. PMID: 22913798 Free PMC article.
-
Coadaptation revisited.J Hered. 1991 Mar-Apr;82(2):89-95. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a111061. J Hered. 1991. PMID: 1901579 Review.
-
Gene regulation by chromatin structure: paradigms established in Drosophila melanogaster.Annu Rev Entomol. 2007;52:171-92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ento.51.110104.151007. Annu Rev Entomol. 2007. PMID: 16881818 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Evolution of Drosophila Germline Stem Cell and Neural Stem Cell Regulating Genes.Genome Biol Evol. 2015 Oct 27;7(11):3097-114. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv207. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 26507797 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb group proteins confer robustness to aposematic coloration in the milkweed bug, Oncopeltus fasciatus.Proc Biol Sci. 2024 Aug;291(2028):20240713. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2024.0713. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Proc Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39106954 Free PMC article.
-
Histone methylation regulates reproductive diapause in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS Genet. 2023 Sep 13;19(9):e1010906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010906. eCollection 2023 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37703303 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome expression plasticity across tropical and temperate Drosophila melanogaster populations from Eastern Australia.Mol Biol Evol. 2011 Jan;28(1):249-56. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq197. Epub 2010 Jul 29. Mol Biol Evol. 2011. PMID: 20671040 Free PMC article.
-
Segregating variation in the polycomb group gene cramped alters the effect of temperature on multiple traits.PLoS Genet. 2011 Jan 20;7(1):e1001280. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001280. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21283785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allis, C. D., T. Jenuwein, D. Reinberg and M. Caparros, 2007. Epigenetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
-
- Ashburner, M., 1967. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. I. Autosomal puffing patterns in a laboratory stock of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 21 398–428. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner, M., 1970. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. V. Responses to environmental treatments. Chromosoma 31 356–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

