Adaptive functional divergence among triplicated alpha-globin genes in rodents
- PMID: 18245844
- PMCID: PMC2278084
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.080903
Adaptive functional divergence among triplicated alpha-globin genes in rodents
Abstract
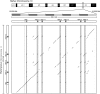
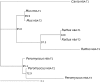
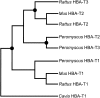
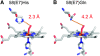
The functional divergence of duplicated genes is thought to play an important role in the evolution of new developmental and physiological pathways, but the role of positive selection in driving this process remains controversial. The objective of this study was to test whether amino acid differences among triplicated alpha-globin paralogs of the Norway rat (Rattus norvegicus) and the deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) are attributable to a relaxation of purifying selection or to a history of positive selection that has adapted the gene products to new or modified physiological tasks. In each rodent species, the two paralogs at the 5'-end of the alpha-globin gene cluster (HBA-T1 and HBA-T2) are evolving in concert and are therefore identical or nearly identical in sequence. However, in each case, the HBA-T1 and HBA-T2 paralogs are distinguished from the third paralog at the 3'-end of the gene cluster (HBA-T3) by multiple amino acid substitutions. An analysis of genomic sequence data from several rodent species revealed that the HBA-T3 genes of Rattus and Peromyscus originated via independent, lineage-specific duplication events. In the independently derived HBA-T3 genes of both species, a likelihood analysis based on a codon-substitution model revealed that accelerated rates of amino acid substitution are attributable to positive directional selection, not to a relaxation of purifying selection. As a result of functional divergence among the triplicated alpha-globin genes in Rattus and Peromyscus, the red blood cells of both rodent species contain a mixture of functionally distinct alpha-chain hemoglobin isoforms that are predicted to have different oxygen-binding affinities. In P. maniculatus, a species that is able to sustain physiological function under conditions of chronic hypoxia at high altitude, the coexpression of distinct hemoglobin isoforms with graded oxygen affinities is expected to broaden the permissible range of arterial oxygen tensions for pulmonary/tissue oxygen transport.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Relaxed functional constraints on triplicate α-globin gene in the bank vole suggest a different evolutionary history from other rodents.Heredity (Edinb). 2014 Jul;113(1):64-73. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2014.12. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Heredity (Edinb). 2014. PMID: 24595364 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of duplicated beta-globin genes and the structural basis of hemoglobin isoform differentiation in Mus.Mol Biol Evol. 2009 Nov;26(11):2521-32. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msp165. Epub 2009 Aug 12. Mol Biol Evol. 2009. PMID: 19675095 Free PMC article.
-
Intraspecific polymorphism, interspecific divergence, and the origins of function-altering mutations in deer mouse hemoglobin.Mol Biol Evol. 2015 Apr;32(4):978-97. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu403. Epub 2015 Jan 2. Mol Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25556236 Free PMC article.
-
Gene duplication, genome duplication, and the functional diversification of vertebrate globins.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2013 Feb;66(2):469-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2012.07.013. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2013. PMID: 22846683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phylogenetic diversification of the globin gene superfamily in chordates.IUBMB Life. 2011 May;63(5):313-22. doi: 10.1002/iub.482. Epub 2011 May 9. IUBMB Life. 2011. PMID: 21557448 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome evolution: gene duplication and the resolution of adaptive conflict.Heredity (Edinb). 2009 Feb;102(2):99-100. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2008.114. Epub 2008 Oct 29. Heredity (Edinb). 2009. PMID: 18971957 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lineage-specific patterns of functional diversification in the alpha- and beta-globin gene families of tetrapod vertebrates.Mol Biol Evol. 2010 May;27(5):1126-38. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msp325. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Mol Biol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20047955 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic differences in hemoglobin function between highland and lowland deer mice.J Exp Biol. 2010 Aug 1;213(Pt 15):2565-74. doi: 10.1242/jeb.042598. J Exp Biol. 2010. PMID: 20639417 Free PMC article.
-
An Insect Counteradaptation against Host Plant Defenses Evolved through Concerted Neofunctionalization.Mol Biol Evol. 2019 May 1;36(5):930-941. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msz019. Mol Biol Evol. 2019. PMID: 30715408 Free PMC article.
-
Copy number polymorphism in the α-globin gene cluster of European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus).Heredity (Edinb). 2012 May;108(5):531-6. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2011.118. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Heredity (Edinb). 2012. PMID: 22146981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguileta, G., J. P. Bielawski and Z. H. Yang, 2004. Gene conversion and functional divergence in the beta-globin gene family. J. Mol. Evol. 59 177–189. - PubMed
-
- Aguileta, G., J. P. Bielawski and Z. H. Yang, 2006. Proposed standard nomenclature for the alpha- and beta-globin gene families. Genes Genet. Syst. 81 367–371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

