Top-down laminar organization of the excitatory network in motor cortex
- PMID: 18246064
- PMCID: PMC2748826
- DOI: 10.1038/nn2049
Top-down laminar organization of the excitatory network in motor cortex
Abstract
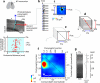
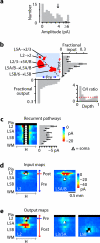
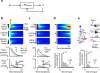
Cortical layering is a hallmark of the mammalian neocortex and a major determinant of local synaptic circuit organization in sensory systems. In motor cortex, the laminar organization of cortical circuits has not been resolved, although their input-output operations are crucial for motor control. Here, we developed a general approach for estimating layer-specific connectivity in cortical circuits and applied it to mouse motor cortex. From these data we computed a laminar presynaptic --> postsynaptic connectivity matrix, W(post,pre), revealing a complement of stereotypic pathways dominated by layer 2 outflow to deeper layers. Network modeling predicted, and experiments with disinhibited slices confirmed, that stimuli targeting upper, but not lower, cortical layers effectively evoked network-wide events. Thus, in motor cortex, descending excitation from a preamplifier-like network of upper-layer neurons drives output neurons in lower layers. Our analysis provides a quantitative wiring-diagram framework for further investigation of the excitatory networks mediating cortical mechanisms of motor control.
Figures
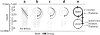
References
-
- Wise SP, Donoghue JP. Cerebral cortex. In: Jones EG, Peters A, editors. Sensory-motor areas and aspects of cortical connectivity. Plenum; New York: 1986. pp. 243–270.
-
- Keller A. Intrinsic synaptic organization of the motor cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1993;3:430–41. - PubMed
-
- Schieber MH. Constraints on somatotopic organization in the primary motor cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2001;86:2125–43. - PubMed
-
- Callaway EM. Local circuits in primary visual cortex of the macaque monkey. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1998;21:47–74. - PubMed
-
- Douglas RJ, Martin KA. Neuronal circuits of the neocortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004;27:419–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

