Coinfection of avian influenza virus (H9N2 subtype) with infectious bronchitis live vaccine
- PMID: 18247102
- PMCID: PMC7086985
- DOI: 10.1007/s00705-008-0033-x
Coinfection of avian influenza virus (H9N2 subtype) with infectious bronchitis live vaccine
Abstract
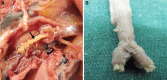
Avian influenza virus of H9N2 subtype is pathotyped as a non-highly pathogenic virus. However, frequent incidences of avian influenza of high mortality that are caused by H9N2 viruses have been observed in broiler chicken farms in Iran and some other Asian countries. Coinfections or environmental factors may be involved in such cases. Infectious microorganisms have been implicating in taking part in the cases of coinfection. We studied the effect of experimental coinfection of H9N2 avian influenza virus with infectious bronchitis live vaccine, which is used extensively in chicken farms in Iran. Clinical signs, gross lesions, viral shedding and mortality rate of the experimentally infected birds were examined. Coinfection of infectious bronchitis live vaccine and H9N2 avian influenza virus led to an extension of the shedding period of H9N2 virus, increasing the severity of clinical signs and mortality rates, causing macroscopic lesions in the embryos.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Co-infections of chickens with avian influenza virus H9N2 and Moroccan Italy 02 infectious bronchitis virus: effect on pathogenesis and protection conferred by different vaccination programmes.Avian Pathol. 2020 Feb;49(1):21-28. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2019.1656328. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Avian Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31412705
-
Co-infection of H9N2 subtype avian influenza virus and QX genotype live attenuated infectious bronchitis virus increase the pathogenicity in SPF chickens.Vet Microbiol. 2024 Aug;295:110163. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2024.110163. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Vet Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38959807
-
Experimental co-infection of infectious bronchitis and low pathogenic avian influenza H9N2 viruses in commercial broiler chickens.Res Vet Sci. 2017 Dec;115:356-362. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2017.06.024. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Res Vet Sci. 2017. PMID: 28692924 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory disease complex due to mixed viral infections in chicken in Jordan.Poult Sci. 2024 Apr;103(4):103565. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103565. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38417340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral responses against chicken respiratory infections: Focus on avian influenza virus and infectious bronchitis virus.Cytokine. 2020 Mar;127:154961. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154961. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 31901597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the haemagglutinin genes of H9N2 avian influenza viruses isolated from commercial chickens in Iran.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2010 Aug;42(6):1291-7. doi: 10.1007/s11250-010-9565-7. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2010. PMID: 20390351
-
Predominance of low pathogenic avian influenza virus H9N2 in the respiratory co-infections in broilers in Tunisia: a longitudinal field study, 2018-2020.Vet Res. 2023 Oct 3;54(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13567-023-01204-7. Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 37789451 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characteristics and pathogenicity analysis of QX-like avian infectious bronchitis virus isolated in China in 2017 and 2018.Poult Sci. 2019 Nov 1;98(11):5336-5341. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez351. Poult Sci. 2019. PMID: 31222258 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and Application of Mismatch Amplification Mutation Assay-PCR for Rapid Detection and Differentiation of Duck Hepatitis A Virus-1 Attenuated Vaccine and Wild Strains.Animals (Basel). 2024 Sep 21;14(18):2733. doi: 10.3390/ani14182733. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335322 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into the Host-Pathogen Interaction of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Avian Metapneumovirus in Tracheal Organ Cultures of Chicken.Microorganisms. 2021 Nov 22;9(11):2407. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9112407. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34835532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander DJ. Avian influenza: recent developments. Vet Bull. 1982;52:341–359.
-
- Bano S, Naeem K, Malik SA. Evaluation of pathogenic potential of avian influenza virus serotype H9N2 in chickens. Avian Dis. 2003;47:817–822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

