TRIM E3 ligases interfere with early and late stages of the retroviral life cycle
- PMID: 18248090
- PMCID: PMC2222954
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0040016
TRIM E3 ligases interfere with early and late stages of the retroviral life cycle
Abstract
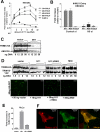
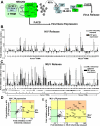
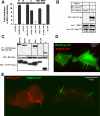
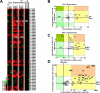
Members of the TRIpartite interaction Motif (TRIM) family of E3 ligases have been shown to exhibit antiviral activities. Here we report a near comprehensive screen for antiretroviral activities of 55 TRIM proteins (36 human, 19 mouse). We identified approximately 20 TRIM proteins that, when transiently expressed in HEK293 cells, affect the entry or release of human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV), murine leukemia virus (MLV), or avian leukosis virus (ALV). While TRIM11 and 31 inhibited HIV entry, TRIM11 enhanced N-MLV entry by interfering with Ref1 restriction. Strikingly, many TRIM proteins affected late stages of the viral life cycle. Gene silencing of endogenously expressed TRIM 25, 31, and 62 inhibited viral release indicating that they play an important role at late stages of the viral life cycle. In contrast, downregulation of TRIM11 and 15 enhanced virus release suggesting that these proteins contribute to the endogenous restriction of retroviruses in cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Goff SP. Host factors exploited by retroviruses. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5:253–263. - PubMed
-
- Nisole S, Stoye JP, Saib A. TRIM family proteins: retroviral restriction and antiviral defence. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3:799–808. - PubMed
-
- Towers GJ, Goff SP. Post-entry restriction of retroviral infections. AIDS Rev. 2003;5:156–164. - PubMed
-
- Bieniasz PD. Intrinsic immunity: a front-line defense against viral attack. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:1109–1115. - PubMed
-
- Sokolskaja E, Luban J. Cyclophilin, TRIM5, and innate immunity to HIV-1. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006;9:404–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

