Inhibition of monoamine oxidase A promotes secretory differentiation in basal prostatic epithelial cells
- PMID: 18248494
- PMCID: PMC2760409
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.2007.00263.x
Inhibition of monoamine oxidase A promotes secretory differentiation in basal prostatic epithelial cells
Abstract
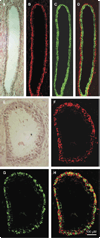
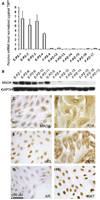
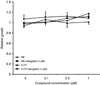
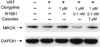
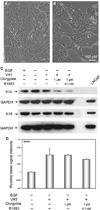
Monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) expression is associated with high-grade prostate cancer. Immunohistochemistry showed that MAO-A is also expressed in the basal epithelial cells of normal prostate glands. Using cultured primary prostatic epithelial cells as a model, we showed that MAO-A prevents basal epithelial cells from differentiating into secretory cells. Under differentiation-promoting conditions, clorgyline, an irreversible MAO-A inhibitor, induced secretory cell-like morphology and repressed expression of cytokeratin 14, a basal cell marker. More importantly, clorgyline induced mRNA and protein expression of androgen receptor (AR), a hallmark of secretory epithelial cells. In clorgyline-treated cells, androgen induced luciferase activity controlled by the promoter of prostate-specific antigen, an AR target gene, in a dose-dependent manner. This activity was blocked by the AR antagonist Casodex, showing that AR is functional. In turn, androgen decreased MAO-A expression in clorgyline-treated, secretory-like cells. Our results demonstrated that cultured basal epithelial cells have the potential to differentiate into secretory cells, and that inhibition of MAO-A is a key factor in promoting this process. Increased expression of MAO-A in high-grade prostate cancer may be an important contributor to its de-differentiated phenotype, raising the possibility that MAO-A inhibition may restore differentiation and reverse the aggressive behavior of high-grade cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Abrahamsson PA, di Sant’Agnese PA. Neuroendocrine cells in the human prostate gland. J Androl. 1993;14:307–309. - PubMed
-
- Berger R, Febbo PG, Majumder PK, Zhao JJ, Mukherjee S, Signoretti S, Campbell KT, Sellers WR, Roberts TM, Loda M, Golub TR, Hahn WC. Androgen-in-duced differentiation and tumorigenicity of human prostate epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:8867–8875. - PubMed
-
- Bonkhoff H, Stein U, Remberger K. Multidirectional differentiation in the normal, hyperplastic, and neoplastic human prostate: simultaneous demonstration of cell-specific epithelial markers. Hum Pathol. 1994;25:42–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

