Statins reduce neuronal alpha-synuclein aggregation in in vitro models of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 18248604
- PMCID: PMC2822545
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05254.x
Statins reduce neuronal alpha-synuclein aggregation in in vitro models of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Aggregation of alpha-synuclein (alpha-syn) is believed to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of disorders such as dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease. The function of alpha-syn remains unclear, although several lines of evidence suggest that alpha-syn is involved in synaptic vesicle trafficking probably via lipid binding. Moreover, interactions with cholesterol and lipids have been shown to be involved in alpha-syn aggregation. In this context, the main objective of this study was to determine if statins--cholesterol synthesis inhibitors--might interfere with alpha-syn accumulation in cellular models. For this purpose, we studied the effects of lovastatin, simvastatin, and pravastatin on the accumulation of alpha-syn in a stably transfected neuronal cell line and in primary human neurons. Statins reduced the levels of alpha-syn accumulation in the detergent insoluble fraction of the transfected cells. This was accompanied by a redistribution of alpha-syn in caveolar fractions, a reduction in oxidized alpha-syn, and enhanced neurite outgrowth. In contrast, supplementation of the media with cholesterol increased alpha-syn aggregation in detergent insoluble fractions of transfected cells and was accompanied by reduced neurite outgrowth. Taken together, these results suggest that regulation of cholesterol levels with cholesterol inhibitors might be a novel approach for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Figures




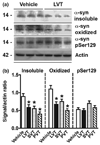
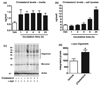
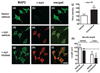
References
-
- Bar-On P, Rockenstein E, Adame A, Ho G, Hashimoto M, Masliah E. Effects of the cholesterol-lowering compound methyl-beta-cyclodextrin in models of alpha-synucleinopathy. J. Neurochem. 2006;98:1032–1045. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and coenzyme Q10 as a potential treatment. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2004;36:381–386. - PubMed
-
- Bieschke J, Zhang Q, Bosco DA, Lerner RA, Powers ET, Wentworth P, Jr, Kelly JW. Small molecule oxidation products trigger disease-associated protein misfolding. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006;39:611–619. - PubMed
-
- Binkowski-Machut C, Hapiot F, Martin P, Cecchelli R, Monflier E. How cyclodextrins can mask their toxic effect on the blood-brain barrier. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006;16:1784–1787. - PubMed
-
- Bosco DA, Fowler DM, Zhang Q, Nieva J, Powers ET, Wentworth P, Jr, Lerner RA, Kelly JW. Elevated levels of oxidized cholesterol metabolites in Lewy body disease brains accelerate alpha-synuclein fibrilization. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006;2:249–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

