Parallel transport in diffeomorphisms distinguishes the time-dependent pattern of hippocampal surface deformation due to healthy aging and the dementia of the Alzheimer's type
- PMID: 18249009
- PMCID: PMC3517912
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.11.041
Parallel transport in diffeomorphisms distinguishes the time-dependent pattern of hippocampal surface deformation due to healthy aging and the dementia of the Alzheimer's type
Abstract
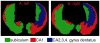
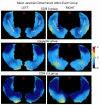
Hippocampal surface structure was assessed at twice 2 years apart in 26 nondemented subjects (CDR 0), in 18 subjects with early dementia of Alzheimer type (DAT, CDR 0.5), and in 9 subjects who converted from the nondemented (CDR 0) to the demented (CDR 0.5) state using magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. We used parallel transport in diffeomorphisms under the large deformation diffeomorphic metric mapping framework to translate within-subject deformation of the hippocampal surface as represented in the MR images between the two time points in a global template coordinate system. We then performed hypothesis testing on the longitudinal variation of hippocampal shape in the global template. Both subjects with early DAT and converters showed greater rates of hippocampal deformation across time than nondemented controls within every subfield of the hippocampus. In a random field analysis, inward surface deformation across time occurred in a non-uniform manner across the hippocampal surface in subjects with early DAT relative to the nondemented controls. Also, compared to the controls, the lateral aspect of the left hippocampal tail showed inward surface deformation in the converters. Using surface deformation patterns as features in a linear discriminant analysis, we were able to respectively distinguish converters and patients with early DAT from healthy nondemented controls at classification rates of 0.77 and 0.87, which were obtained in the same training set using the leave-one-out cross validation approach.
Figures


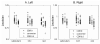

References
-
- Apostolova LG, Dinov ID, Dutton RA, Hayashi KM, Toga AW, Cummings JL, Thompson PM. 3D comparison of hippocampal atrophy in amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2006a;129:2867–2873. - PubMed
-
- Apostolova LG, Dutton RA, Dinov ID, Hayashi KM, Toga AW, Cummings JL, Thompson PM. Conversion of mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer disease predicted by hippocampal atrophy maps. Arch Neurol. 2006b;63:693–699. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Andersson JL, Friston KJ. High-dimensional image registration using symmetric priors. Neuroimage. 1999;9:619–628. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Voxel-based morphometry--the methods. Neuroimage. 2000;11:805–821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH064838/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG 025824/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025824/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 O60883/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 EB000975/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR015241/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060883/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB 00975/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH071616/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR 15241/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH 071616/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 064838/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG 05681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG 03991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

