Hepatic insulin resistance is sufficient to produce dyslipidemia and susceptibility to atherosclerosis
- PMID: 18249172
- PMCID: PMC4251554
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.11.013
Hepatic insulin resistance is sufficient to produce dyslipidemia and susceptibility to atherosclerosis
Abstract
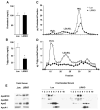
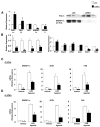
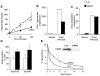
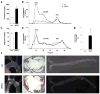
Insulin resistance plays a central role in the development of the metabolic syndrome, but how it relates to cardiovascular disease remains controversial. Liver insulin receptor knockout (LIRKO) mice have pure hepatic insulin resistance. On a standard chow diet, LIRKO mice have a proatherogenic lipoprotein profile with reduced high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles that are markedly enriched in cholesterol. This is due to increased secretion and decreased clearance of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins, coupled with decreased triglyceride secretion secondary to increased expression of Pgc-1 beta (Ppargc-1b), which promotes VLDL secretion, but decreased expression of Srebp-1c (Srebf1), Srebp-2 (Srebf2), and their targets, the lipogenic enzymes and the LDL receptor. Within 12 weeks on an atherogenic diet, LIRKO mice show marked hypercholesterolemia, and 100% of LIRKO mice, but 0% of controls, develop severe atherosclerosis. Thus, insulin resistance at the level of the liver is sufficient to produce the dyslipidemia and increased risk of atherosclerosis associated with the metabolic syndrome.
Figures
Comment in
-
Selective versus total insulin resistance: a pathogenic paradox.Cell Metab. 2008 Feb;7(2):95-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.12.009. Cell Metab. 2008. PMID: 18249166 Review.
References
-
- Argmann CA, Houten SM, Champy MF, Auwerx J. Lipid and Bile Acid Analysis. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2006. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology; pp. 29B.2.1–29B.2.24. - PubMed
-
- Babaev VR, Patel MB, Semenkovich CF, Fazio S, Linton MF. Macrophage lipoprotein lipase promotes foam cell formation and atherosclerosis in low density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:26293–26299. - PubMed
-
- Bartels ED, Lauritsen M, Nielsen LB. Hepatic expression of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein and in vivo secretion of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins are increased in obese diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2002;51:1233–1239. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartl J, Baudler S, Scherner M, Babaev V, Makowski L, Suttles J, McDuffie M, Tobe K, Kadowaki T, Fazio S, Kahn CR, Hotamisligil GS, Krone W, Linton M, Bruning JC. Myeloid lineage cell-restricted insulin resistance protects apolipoprotein E-deficient mice against atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 2006;3:247–256. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biddinger SB, Almind K, Miyazaki M, Kokkotou E, Ntambi JM, Kahn CR. Effects of diet and genetic background on sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1, and the development of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes. 2005;54:1314–1323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL55368/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK45935/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056626/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK59637-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK053105/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073030/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK048873/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK031036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075850/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073687/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK75850/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK36836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK036836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08DK073358/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK31036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053105/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK048873/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12 DK063696/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK073687/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL73030/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK036588/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK045935/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK031036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

