Cortico-cortical networks in patients with ideomotor apraxia as revealed by EEG coherence analysis
- PMID: 18249498
- PMCID: PMC2276599
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.12.065
Cortico-cortical networks in patients with ideomotor apraxia as revealed by EEG coherence analysis
Erratum in
- Neurosci Lett. 2009 Jan 16;449(3):259
Abstract
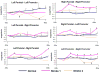
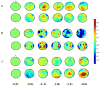
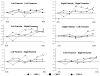
We sought to determine whether coherent networks which circumvent lesioned cortex are seen in patients with ideomotor apraxia (IMA) while performing tool-use pantomimes. Five normal subjects and five patients with IMA (three patients with corticobasal degeneration and two with left hemisphere stroke) underwent 64-channel EEG recording while performing three tool-use pantomimes with their left hand in a self-paced manner. Beta band (20-22 Hz) coherence indicates that normal subjects have a dominant left hemisphere network responsible for praxis preparation, which was absent in patients. Corticobasal degeneration patients showed significant coherence increase between left parietal-right premotor areas. Left hemisphere stroke patients showed significant coherence increases in a right parietofrontal network. The right hemisphere appears to store useable praxis representations in IMA patients with left hemisphere damage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Left inferior parietal representations for skilled hand-object interactions: evidence from stroke and corticobasal degeneration.Cortex. 2007 Apr;43(3):411-23. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(08)70466-0. Cortex. 2007. PMID: 17533764
-
Inter- and intrahemispheric dissociations in ideomotor apraxia: a large-scale lesion-symptom mapping study in subacute brain-damaged patients.Cereb Cortex. 2013 Dec;23(12):2781-9. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs280. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Cereb Cortex. 2013. PMID: 22989580
-
Dysfunction of the Human Mirror Neuron System in Ideomotor Apraxia: Evidence from Mu Suppression.J Cogn Neurosci. 2016 Jun;28(6):775-91. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00936. Epub 2016 Mar 4. J Cogn Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26942323
-
Limb apraxia.Semin Neurol. 2000;20(4):471-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-13180. Semin Neurol. 2000. PMID: 11149703 Review.
-
Ideomotor apraxia: a review.J Neurol Sci. 2007 Sep 15;260(1-2):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2007.04.014. Epub 2007 May 16. J Neurol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17507030 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of tDCS on corticomuscular coupling and the brain functional network of stroke patients.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2023 Dec;61(12):3303-3317. doi: 10.1007/s11517-023-02905-z. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2023. PMID: 37667074
-
Dynamics of functional and effective connectivity within human cortical motor control networks.Clin Neurophysiol. 2015 May;126(5):987-96. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.09.006. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25270239 Free PMC article.
-
Altered task-related modulation of long-range connectivity in children with autism.Autism Res. 2018 Feb;11(2):245-257. doi: 10.1002/aur.1858. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Autism Res. 2018. PMID: 28898569 Free PMC article.
-
Gesture subtype-dependent left lateralization of praxis planning: an event-related fMRI study.Cereb Cortex. 2009 Jun;19(6):1256-62. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhn168. Epub 2008 Sep 16. Cereb Cortex. 2009. PMID: 18796430 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-frequency and iso-frequency estimation of functional corticomuscular coupling after stroke.Cogn Neurodyn. 2021 Jun;15(3):439-451. doi: 10.1007/s11571-020-09635-0. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Cogn Neurodyn. 2021. PMID: 34040670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basso A, Capitani E, Della Sala S, Laiacona M, Spinnler H. Ideomotor apraxia: a study of initial severity. Acta Neurol Scand. 1987;76:142–6. - PubMed
-
- Bernal B, Ardila A, Altman N. Acalculia: an fMRI study with implications with respect to brain plasticity. Int J Neurosci. 2003;113:1505–23. - PubMed
-
- Cavada C, Goldman-Rakic PS. Posterior parietal cortex in rhesus monkey: I. Parcellation of areas based on distinctive limbic and sensory corticocortical connections. J Comp Neurol. 1989;287:393–421. - PubMed
-
- Cavada C, Goldman-Rakic PS. Posterior parietal cortex in rhesus monkey: II. Evidence for segregated corticocortical networks linking sensory and limbic areas with the frontal lobe. J Comp Neurol. 1989;287:422–45. - PubMed
-
- Crosson B, Moore AB, Gopinath K, White KD, Wierenga CE, Gaiefsky ME, Fabrizio KS, Peck KK, Soltysik D, Milsted C, Briggs RW, Conway TW, Gonzalez Rothi LJ. Role of the right and left hemispheres in recovery of function during treatment of intention in aphasia. J Cogn Neurosci. 2005;17:392–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

