Phosphorylation of LKB1 at serine 428 by protein kinase C-zeta is required for metformin-enhanced activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase in endothelial cells
- PMID: 18250273
- PMCID: PMC2862466
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.744490
Phosphorylation of LKB1 at serine 428 by protein kinase C-zeta is required for metformin-enhanced activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase in endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Metformin, one of most commonly used antidiabetes drugs, is reported to exert its therapeutic effects by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK); however, the mechanism by which metformin activates AMPK is poorly defined. The objective of the present study was to determine how metformin activates AMPK in endothelial cells.
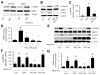
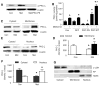
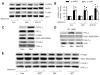
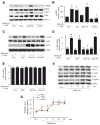
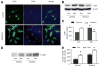
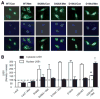
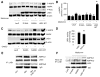
Methods and results: Exposure of human umbilical vein endothelial cells or bovine aortic endothelial cells to metformin significantly increased AMPK activity and the phosphorylation of both AMPK at Thr172 and LKB1 at Ser428, an AMPK kinase, which was paralleled by increased activation of protein kinase C (PKC)-zeta, as evidenced by increased activity, phosphorylation (Thr410/403), and nuclear translocation of PKC-zeta. Consistently, either pharmacological or genetic inhibition of PKC-zeta ablated metformin-enhanced phosphorylation of both AMPK-Thr172 and LKB1-Ser428, suggesting that PKC-zeta might act as an upstream kinase for LKB1. Furthermore, adenoviral overexpression of LKB1 kinase-dead mutants abolished but LKB1 wild-type overexpression enhanced the effects of metformin on AMPK in bovine aortic endothelial cells. In addition, metformin increased the phosphorylation and nuclear export of LKB1 into the cytosols as well as the association of AMPK with LKB1 in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Similarly, overexpression of LKB1 wild-type but not LKB1 S428A mutants (serine replaced by alanine) restored the effects of metformin on AMPK in LKB1-deficient HeLa-S3 cells, suggesting that Ser428 phosphorylation of LKB1 is required for metformin-enhanced AMPK activation. Moreover, LKB1 S428A, like kinase-dead LKB1 D194A, abolished metformin-enhanced LKB1 translocation as well as the association of LKB1 with AMPK in HeLa-S3 cells. Finally, inhibition of PKC-zeta abolished metformin-enhanced coimmunoprecipitation of LKB1 with both AMPKalpha1 and AMPKalpha2.
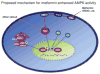
Conclusions: We conclude that PKC-zeta phosphorylates LKB1 at Ser428, resulting in LKB1 nuclear export and hence AMPK activation.
Figures
References
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34) Lancet. 1998;352:854–865. - PubMed
-
- Abbasi F, Chu JW, McLaughlin T, Lamendola C, Leary ET, Reaven GM. Effect of metformin treatment on multiple cardiovascular disease risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2004;53:159–164. - PubMed
-
- Verma S, Yao L, Dumont AS, McNeill JH. Metformin treatment corrects vascular insulin resistance in hypertension. J Hypertens. 2000;8:1445–1450. - PubMed
-
- Katakam PV, Ujhelyi MR, Hoenig M, Miller AW. Metformin improves vascular function in insulin-resistant rats. Hypertension. 2000;35:108–112. - PubMed
-
- Marfella R, Acampora R, Verrazzo G, Ziccardi P, De RN, Giunta R, Giugliano D. Metformin improves hemodynamic and rheological responses to L-arginine in NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care. 1996;19:934–939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL074399/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089920/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074399/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL080499/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL079584/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079584/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1P20RR024215-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL096032/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL110488/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105157/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR024215/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080499/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

