Copeptin, a novel prognostic biomarker in ventilator-associated pneumonia
- PMID: 18252006
- PMCID: PMC2374597
- DOI: 10.1186/cc6780
Copeptin, a novel prognostic biomarker in ventilator-associated pneumonia
Abstract
Background: The present study sought to investigate the correlation of copeptin with the severity of septic status in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), and to analyze the usefulness of copeptin as a predictor of mortality in VAP.
Methods: The prospective observational cohort study was conducted in a teaching hospital. The subjects were 71 patients consecutively admitted to the intensive care unit from October 2003 to August 2005 who developed VAP. Copeptin levels were determined on day 0 and day 4 of VAP. Patients were followed for 28 days after the diagnosis, when they were considered survivors. Patients who died before day 28 were classified as nonsurvivors. There were no interventions.
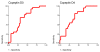
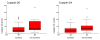
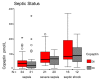
Results: Copeptin levels increased from sepsis to severe sepsis and septic shock both on day 0 and day 4 (P = 0.001 and P = 0.009, respectively). Variables included in the univariable logistic regression analysis for mortality were age, gender, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score and ln copeptin on day 0 and day 4. Mortality was directly related to ln copeptin levels on day 0 and day 4, with odds ratios of 2.32 (95% confidence interval, 1.25 to 4.29) and 2.31 (95% confidence interval, 1.25 to 4.25), respectively. In a multivariable logistic regression model for mortality, only ln copeptin on day 0 with odds ratio 1.97 (95% confidence interval, 1.06 to 3.69) and ln copeptin on day 4 with odds ratio 2.39 (95% confidence interval, 1.24 to 4.62) remained significant.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate that copeptin levels increase progressively with the severity of sepsis and are independent predictors of mortality in VAP.
Figures
Comment in
-
Copeptin: a new and promising diagnostic and prognostic marker.Crit Care. 2008;12(2):117. doi: 10.1186/cc6799. Epub 2008 Mar 6. Crit Care. 2008. PMID: 18355399 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

