Rickettsia monacensis and human disease, Spain
- PMID: 18252123
- PMCID: PMC2857266
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1309.060186
Rickettsia monacensis and human disease, Spain
Abstract
We identified Rickettsia monacensis as a cause of acute tickborne rickettsiosis in 2 humans. Its pathogenic role was assessed by culture and detection of the organism in patients' blood samples. This finding increases the number of recognized human rickettsial pathogens and expands the known geographic distribution of Mediterranean spotted fever-like cases.
Figures
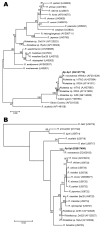
References
-
- Márquez FJ, Muniain MA, Soriguer RC, Izquierdo G, Rodríguez-Bano J, Borobio MV. Genotypic identification of an undescribed spotted fever group rickettsia in Ixodes ricinus from southwestern Spain. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1998;58:570–7. - PubMed
-
- Ishikura M, Ando S, Shinagawa Y, Matsuura K, Hasegawa S, Nakayama T, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of spotted fever group rickettsiae based on gltA, 17-kDa, and rOmpA genes amplified by nested PCR from ticks in Japan. Microbiol Immunol. 2003;47:823–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
