COMT val158met genotype affects recruitment of neural mechanisms supporting fluid intelligence
- PMID: 18252743
- PMCID: PMC2517101
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhm240
COMT val158met genotype affects recruitment of neural mechanisms supporting fluid intelligence
Abstract
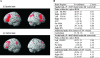
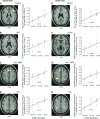
Fluid intelligence (g(f)) influences performance across many cognitive domains. It is affected by both genetic and environmental factors. Tasks tapping g(f) activate a network of brain regions including the lateral prefrontal cortex (LPFC), the presupplementary motor area/anterior cingulate cortex (pre-SMA/ACC), and the intraparietal sulcus (IPS). In line with the "intermediate phenotype" approach, we assessed effects of a polymorphism (val(158)met) in the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) gene on activity within this network and on actual task performance during spatial and verbal g(f) tasks. COMT regulates catecholaminergic signaling in prefrontal cortex. The val(158) allele is associated with higher COMT activity than the met(158) allele. Twenty-two volunteers genotyped for the COMT val(158)met polymorphism completed high and low g(f) versions of spatial and verbal problem-solving tasks. Our results showed a positive effect of COMT val allele load upon the blood oxygen level-dependent response in LPFC, pre-SMA/ACC, and IPS during high g(f) versus low g(f) task performance in both spatial and verbal domains. These results indicate an influence of the COMT val(158)met polymorphism upon the neural circuitry supporting g(f). The behavioral effects of val allele load differed inside and outside the scanner, consistent with contextual modulation of the relation between COMT val(158)met genotype and g(f) task performance.
Figures
References
-
- Ackerman PL, Beier ME, Boyle MO. Working memory and intelligence: the same or different constructs? Psychol Bull. 2005;131:30–60. - PubMed
-
- Arnsten AF, Goldman-Rakic PS. Noise stress impairs prefrontal cortical cognitive function in monkeys: evidence for a hyperdopaminergic mechanism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55:362–368. - PubMed
-
- Barnett JH, Jones PB, Robbins TW, Muller U. Effects of the catechol-O-methyltransferase Val158Met polymorphism on executive function: a meta-analysis of the Wisconsin Card Sort Test in schizophrenia and healthy controls. Mol Psychiatry. 2007;12:502–509. - PubMed
-
- Bentivoglio M, Morelli M. The organization and circuits of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons and the distribution of dopamine receptors in the brain. In: Dunnett SB, Bentivoglio M, Bjorklund A, Hokfelt T, editors. Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy. Vol. 21. Dopamine. Amsterdam (NL): Elsevier; 2005. pp. 1–107.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

