Quantitative assessment of synovial vascularity using contrast-enhanced power Doppler ultrasonography: correlation with histologic findings and mr imaging findings in arthritic rabbit knee model
- PMID: 18253075
- PMCID: PMC2627181
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2008.9.1.45
Quantitative assessment of synovial vascularity using contrast-enhanced power Doppler ultrasonography: correlation with histologic findings and mr imaging findings in arthritic rabbit knee model
Abstract
Objective: To validate contrast-enhanced power Doppler ultrasonography (PD US) for the evaluation of synovial vascularity in an arthritic rabbit knee model in correlation with MR and histological findings.
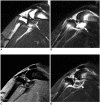
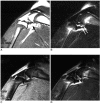
Materials and methods: Power Doppler ultrasonography was performed for carrageenin-induced arthritic left knee and control right knee of 13 rabbits, first without and then with sonic contrast agent enhancement (Levovist, Schering, Berlin Germany), followed by gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging. Synovial vascularity was quantitatively assessed by calculating the color pixel area in power Doppler sonography using a computer-aided image analysis program and by grading the enhancement on MR images: grade 1, enhancement of knee joint is less than one-third of the area; grade 2, one-third to two-thirds enhancement; and grade 3, more than two-thirds enhancement. Microvessel density (MVD) was measured on slides stained immunohistochemically for CD31 antigen for histological assessment.
Results: The mean area of color pixels in PD US changed from 4.37 to 16.42 mm(2) in the arthritic knee after enhancement (p < 0.05), whereas it changed from 0.77 to 2.31 mm(2) in the control knee (p < 0.05). Arthritic knees had greater power Doppler signal than control knees both before and after contrast administration (p < 0.05). The average MVD was 88 in arthritic knees and 46 in control knees. MVDs correlated with color pixel areas of contrast-enhanced power Doppler imaging in arthritic knees. In MR grading of arthritic knees, five were grade 2 and eight were grade 3. MVD and PD US revealed no significant difference between grade 2 and 3 arthritic knees (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Sonic contrast-enhanced PD US improves the visualization of synovial vascularity and allows quantitative measurement in experimentally induced rabbit arthritic knees.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Longitudinal Changes in Knee Joint Synovial Vascularity in a Rabbit Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Quantification Using Power Doppler Ultrasound and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021 Aug;47(8):2430-2441. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2021.03.012. Epub 2021 May 3. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33958258
-
Correlation of power Doppler sonography with vascularity of the synovial tissue of the knee joint in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Feb;44(2):331-8. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200102)44:2<331::AID-ANR50>3.0.CO;2-0. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. PMID: 11229463
-
Contrast medium in power Doppler ultrasound for assessment of synovial vascularity: comparison with arthroscopy.J Rheumatol. 2003 Oct;30(10):2170-6. J Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 14528513
-
Are contrast-enhanced and non-contrast MRI findings reflecting synovial inflammation in knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020 Feb;28(2):126-136. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.10.008. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020. PMID: 31678664 Review.
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma: contrast enhancement with Levovist.J Ultrasound Med. 2002 Jan;21(1):77-84. doi: 10.7863/jum.2002.21.1.77. J Ultrasound Med. 2002. PMID: 11794406 Review.
Cited by
-
Contrast-enhanced harmonic ultrasonography for the assessment of prostate cancer aggressiveness: a preliminary study.Korean J Radiol. 2010 Jan-Feb;11(1):75-83. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2010.11.1.75. Epub 2009 Dec 28. Korean J Radiol. 2010. PMID: 20046498 Free PMC article.
-
MR and CEUS monitoring of patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis treated with biological agents: a preliminary study.Radiol Med. 2014 Jun;119(6):422-31. doi: 10.1007/s11547-013-0369-5. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Radiol Med. 2014. PMID: 24347286
-
Value of power Doppler and gray-scale US in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: contribution of cross-sectional area just before the tunnel inlet as compared with the cross-sectional area at the tunnel.Korean J Radiol. 2010 Nov-Dec;11(6):632-9. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2010.11.6.632. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Korean J Radiol. 2010. PMID: 21076589 Free PMC article.
-
Animal model of acute gout reproduces the inflammatory and ultrasonographic joint changes of human gout.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Feb 26;17(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0550-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25889158 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between computerised findings and Newman's scaling on vascularity using power Doppler ultrasonography imaging and its predictive value in patients with plantar fasciitis.Br J Radiol. 2012 Jul;85(1015):925-9. doi: 10.1259/bjr/99342011. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Br J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22167513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pando JA, Duray P, Yarboro C, Gourley MF, Klippel JH, Schumacher HR. Synovitis occurs in some clinically normal and asymptomatic joints in patients with early arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:1848–1854. - PubMed
-
- Harrison BJ, Symmons DP, Barrett EM, Silman AJ. The performance of the 1987 ARA classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis in a population based cohort of patients with early inflammatory polyarthritis. American Rheumatism Association. J Rheumatol. 1998;25:2324–2233. - PubMed
-
- Schumacher HR, Pessler F, Chen LX. Diagnosing early rheumatoid arthritis (RA). What are the problems and opportunities? Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003;21(suppl. 31):S15–SS1. - PubMed
-
- Saaibi DL, Schumacher HR., Jr Percutaneous needle biopsy and synovial histology. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1996;10:535–554. - PubMed
-
- Ostergaard M, Szkudlarek M. Imaging in rheumatoid arthritis - why MRI and ultrasonography can no longer be ignored. Scand J Rheumatol. 2003;32:63–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

