Pharmacological interventions for hypertensive emergencies
- PMID: 18254026
- PMCID: PMC6991936
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003653.pub3
Pharmacological interventions for hypertensive emergencies
Abstract
Background: Hypertensive emergencies, marked hypertension associated with acute end-organ damage, are life-threatening conditions. Many anti-hypertensive drugs have been used in these clinical settings. The benefits and harms of such treatment and the best first-line treatment are not known.
Objectives: To answer the following two questions using randomized controlled trials (RCTs): 1) does anti-hypertensive drug therapy as compared to placebo or no treatment affect mortality and morbidity in patients presenting with a hypertensive emergency? 2) Does one first-line antihypertensive drug class as compared to another antihypertensive drug class affect mortality and morbidity in these patients?
Search strategy: Electronic sources: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane clinical trial register. In addition, we searched for references in review articles and trials. We attempted to contact trialists. Most recent search August 2007.
Selection criteria: All unconfounded, truly randomized trials that compare an antihypertensive drug versus placebo, no treatment, or another antihypertensive drug from a different class in patients presenting with a hypertensive emergency.
Data collection and analysis: Quality of concealment allocation was scored. Data on randomized patients, total serious adverse events, all-cause mortality, non-fatal cardiovascular events, withdrawals due to adverse events, length of follow-up, blood pressure and heart rate were extracted independently and cross checked.
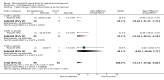
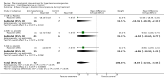
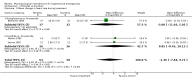
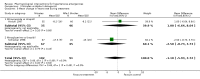
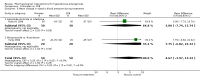
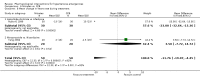
Main results: Fifteen randomized controlled trials (representing 869 patients) met the inclusion criteria. Two trials included a placebo arm. All studies (except one) were open-label trials. Seven drug classes were evaluated in those trials: nitrates (9 trials), ACE-inhibitors (7), diuretics (3), calcium channel blockers (6), alpha-1 adrenergic antagonists (4), direct vasodilators (2) and dopamine agonists (1). Mortality event data were reported in 7 trials. No meta-analysis was performed for clinical outcomes, due to insufficient data. The pooled effect of 3 different anti-hypertensive drugs in one placebo-controlled trial showed a statistically significant greater reduction in both systolic [WMD -13, 95%CI -19,-7] and diastolic [WMD -8, 95%CI, -12,-3] blood pressure with antihypertensive therapy.
Authors' conclusions: There is no RCT evidence demonstrating that anti-hypertensive drugs reduce mortality or morbidity in patients with hypertensive emergencies. Furthermore, there is insufficient RCT evidence to determine which drug or drug class is most effective in reducing mortality and morbidity. There were some minor differences in the degree of blood pressure lowering when one class of antihypertensive drug is compared to another. However, the clinical significance is unknown. RCTs are needed to assess different drug classes to determine initial and longer term mortality and morbidity outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

































Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003653.pub2
References
References to studies included in this review
Angeli 1991 {published data only}
-
- (2) Angeli P, Chiesa M, Caregaro L, Merkel C, Sacerdoti D, Rondana M, et al. Comparison of sublingual captopril and nifedipine in immediate treatment of hypertensive emergencies. A randomized, single‐blind clinical trial. [see comments]. Archives of Internal Medicine 1991;151(4):678‐682. - PubMed
Beltrame 1998 {published data only}
-
- Beltrame JF, Zeitz CJ, Unger SA, Brennan RJ, Hunt A, Moran JL, Horowitz JD. Nitrate therapy is an alternative to furosemide/morphine therapy in the management of acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Journal of Cardiac Failure 1998;4(4):271‐279. - PubMed
DANISH II 1986 {published data only}
-
- Krogsgaard AR, McNair A, Hilden T, Nielsen PE. Reversibility of cerebral symptoms in severe hypertension in relation to acute antihypertensive therapy.Danish Multicenter Study.. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1986;220(1):25‐31. - PubMed
-
- Krogsgaard, A.R, Hilden, T, McNair, A, Nielsen, P.E. Cerebral symptoms and blood pressure during parenteral administration of chlorpromazine, dihydralazine and diazoxide. Danish multicentre study on acute severe hypertension. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1983;Suppl 678:51‐60. - PubMed
-
- McNair A, Krogsgaard AR, Hilden T, Nielsen PE. Severe hypertension with cerebral symptoms treated with furosemide, fractionated diazoxide or dihydralazine. Danish Multicenter Study. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1986;220(1):15‐23. - PubMed
-
- McNair A, Krogsgaard AR, Hilden T, Nielsen PE. Reversibility of cerebral symptoms in severe hypertension in relation to acute antihypertensive therapy. Danish Multicenter study.. Acta medica Scandinavica.Supplementum. 1985;693:107‐110. - PubMed
Elliott 1990 {published data only}
-
- Elliott WJ, Weber RR, Nelson KS, Oliner CM, Fumo MT, Gretler DD, McCray GR, Murphy MB. Renal and hemodynamic effects of intravenous fenoldopam versus nitroprusside in severe hypertension. Circulation 1990;81(3):970‐977. - PubMed
Hamilton 1996 {published data only}
-
- Hamilton RJ, Carter WA, Gallagher EJ. Rapid improvement of acute pulmonary edema with sublingual captopril.[see comment]. Academic Emergency Medicine 1996;3(3):205. - PubMed
Hirschl 1997 {published data only}
-
- Hirschl MM, Binder M, Bur A, Herkner H, Mullner M, Woisetschlager C, Laggner AN. Safety and efficacy of urapidil and sodium nitroprusside in the treatment of hypertensive emergencies. Intensive Care Med 1997;23(8):885‐888. - PubMed
Hirschl 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hirschl MM, Schreiber W, Woisetschlager C, Kaff A, Raab H. [Sublingual nitroglycerin or intravenous enalaprilat in preclinical treatment of hypertensive patients with pulmonary edema]. [German]. Zeitschrift fur Kardiologie 1999;88(3):208‐214. - PubMed
Marigliano 1988 {published data only}
-
- Marigliano V, Santilli D, Fiorani M, Ariani A, Cacciafesta M, Ferri C, Piccirillo G. Hypertensive emergencies in old age: effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition. J Hypertens Suppl 1988;6(1):S91‐S93. - PubMed
Nelson 1983 {published data only}
-
- Nelson GI, Silke B, Ahuja RC, Hussain M, Taylor SH. Haemodynamic advantages of isosorbide dinitrate over frusemide in acute heart‐failure following myocardial infarction. Lancet 1983;1(8327):730‐733. - PubMed
Pastorelli 1991 {published data only}
-
- Pastorelli R, Ferri C, Santucci A, Balsano F. New therapeutic possibilities in hypertensive emergencies. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical & Experimental 1991;50(6):857‐868.
Rubio‐G 1999 {published data only}
-
- Rubio‐Guerra AF, Vargas‐Ayala G, Lozano‐Nuevo JJ, Narvaez‐Rivera JL, Rodriguez‐Lopez L. Comparison between isosorbide dinitrate aerosol and nifedipine in the treatment of hypertensive emergencies. J Hum Hypertens 1999;13(7):473‐476. - PubMed
Schreiber 1998 {published data only}
-
- Schreiber W, Woisetschlager C, Binder M, Kaff A, Raab H, Hirschl MM. The nitura study ‐ Effect of nitroglycerin or urapidil on hemodynamic, metabolic and respiratory parameters in hypertensive patients with pulmonary edema. Intensive Care Med 1998;24(6):557‐563. - PubMed
Verma 1987 {published data only}
-
- Verma SP, Silke B, Hussain M. First‐line treatment of left ventricular failure complicating acute myocardial infarction: A randomised evaluation of immediate effects of diuretic, venodilator, arteriodilator, and positive inotropic drugs on left ventricular function. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology 1987;10(1):38‐46. - PubMed
Wu 1993 {published data only}
-
- Wu SG, Lin SL, Shiao WY, Huang HW, Lin CF, Yang YH. Comparison of sublingual captopril, nifedipine and prazosin in hypertensive emergencies during hemodialysis. Nephron 1993;65(2):284‐287. - PubMed
Yang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Yang HJ, Kim JG, Lim YS, Ryoo E, Hyun SY, Lee G. Nicardipine versus nitroprusside infusion as antihypertensive therapy in hypertensive emergencies. The Journal of international medical research 2004;32(2):118‐123. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Annane 1996 {published data only}
-
- Annane D, Bellissant E, Pussard E, Asmar R, Lacombe F, Lanata E, Madonna O, Safar M, Giudicelli JF, Gajdos P. Placebo‐controlled, randomized, double‐blind study of intravenous enalaprilat efficacy and safety in acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Circulation 1996;94(6):1316‐1324. - PubMed
Bertel 1983 {published data only}
Borghi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Borghi C, Bacchelli S, Esposti DD, Bignamini A, Magnani B, Ambrosioni E. Effects of the administration of an angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor during the acute phase of myocardial infarction in patients with arterial hypertension. SMILE Study Investigators. Survival of Myocardial Infarction Long‐term Evaluation. American journal of hypertension : journal of the American Society of Hypertension 1999;12(7):665‐672. - PubMed
Bussmann 1992 {published data only}
-
- Bussmann WD, Kenedi P, Mengden HJ, Nast HP, Rachor N. Comparison of nitroglycerin with nifedipine in patients with hypertensive crisis or severe hypertension. Clinical Investigator 1992;70(12):1085‐1088. - PubMed
Ceyhan 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ceyhan B, Karaaslan Y, Caymaz O, Oto A, Oram E, Oram A, Ugurlu S. Comparison of sublingual captopril and sublingual nifedipine in hypertensive emergencies. Japanese Journal of Pharmacology 1990;52(2):189‐193. - PubMed
Conen 1988 {published data only}
-
- Conen D, Ruttimann S, Noll G, Schneider K, Muller J. Short‐ and long‐term cerebrovascular effects of nitrendipine in hypertensive patients. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology 1988;12 Suppl 4:S64‐S68. - PubMed
Cotter 1998 {published data only}
-
- Cotter G, Metzkor E, Kaluski E, Faigenberg Z, Miller R, Simovitz A, Shaham O, Marghitay D, Koren M, Blatt A, Moshkovitz Y, Zaidenstein R, Golik A. Randomised trial of high‐dose isosorbide dinitrate plus low‐dose furosemide versus high‐dose furosemide plus low‐dose isosorbide dinitrate in severe pulmonary oedema.[see comment]. Lancet 1998;351(9100):389. - PubMed
Dadkar 1993 {published data only}
-
- Dadkar VN, Karnik ND, Izar M, Sharma SR, Gandhi YP, Narawane NM, Vyawahare SS, Sudhakar S, Gore AG, Kapadia NM. Sublingual nifedipine and captopril in hypertensive urgencies and emergencies. Indian Heart Journal 1993;45(3):185‐187. - PubMed
Franklin 1986 {published data only}
-
- Franklin C, Nightingale S, Mamdani B. A randomized comparison of nifedipine and sodium nitroprusside in severe hypertension. Chest 1986;90(4):500‐503. - PubMed
Guerrera 1990 {published data only}
-
- Guerrera G, Melina D, Capaldi L, Mauro R, Colivicchi F, Cardillo C, Guerrera G, Musumeci V, Savi L, Santoliquido A. [Sublingually administered captopril versus nifedipine in hypertension emergencies]. [Italian]. Minerva Cardioangiologica 1990;38(1‐2):37‐44. - PubMed
Lisk 1993 {published data only}
-
- Lisk DR, Grotta JC, Lamki LM, Tran HD, Taylor JW, Molony DA, Barron BJ. Should hypertension be treated after acute stroke? A randomized controlled trial using single photon emission computed tomography. Archives of Neurology 1993;50(8):855. - PubMed
Marghli 1997 {published data only}
-
- Marghli S, Bouida W, Elatrous S, Boujdaria R, Nouira S, Abroug F. A prospective, randomized and controlled study of three intravenous antihypertensive drugs in severe hypertension. Reanimation Urgences 1997;6(3):289‐296.
Moritz 1989 {published data only}
-
- Moritz RD, Queiroz LP, Pereira MR, Scotinni MA. [Comparative study of the use of nifedipine and captopril in hypertensive emergencies]. [Portuguese]. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia 1989;52(6):323‐326. - PubMed
Nelson 1984 {published data only}
-
- Nelson GI, Verma SP, Silke B, Abdulali S, Taylor SH. Management of hypertension complicating acute myocardial infarction ( MI): comparison of sympathetic (labetalol) and calcium channel ( nifedipine) blockade. [abstract]. Aust NZ J Med Suppl 1984;14(4):577.
Neutel 1994 {published data only}
-
- Neutel JM, Smith DH, Wallin D, Cook E, Ram CV, Fletcher E, Maher KE, Turlepaty P, Grandy S, Lee R. A comparison of intravenous nicardipine and sodium nitroprusside in the immediate treatment of severe hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1994;7(7 Pt 1):623‐628. - PubMed
Nielsen 1980 {published data only}
-
- Nielsen PE, Krogsgaard A, McNair A, Hilden T. Emergency Treatment of Severe Hypertension Evaluated in a Randomized Study. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1980;208:473‐480. - PubMed
Panacek 1995 {published data only}
-
- Panacek EA, Bednarczyk EM, Dunbar LM, Foulke GE, Holcslaw TL. Randomized, prospective trial of fenoldopam vs sodium nitroprusside in the treatment of acute severe hypertension. Fenoldopam Study Group. [see comments]. Academic Emergency Medicine 1995;2(11):959‐965. - PubMed
Pascale 1992 {published data only}
-
- Pascale C, Zampaglione B, Marchisio M. Management of hypertensive crisis: Nifedipine in comparison with captopril, clonidine and furosemide. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical & Experimental 1992;51(1):9‐18.
Perez 1991 {published data only}
-
- Perez C, Dougnac A, Alvarez M, Andresen M, Diaz O, Geni R, Prat G, Vasquez M. [Sublingual captopril versus nifedipine in the treatment of hypertensive crisis]. [Spanish]. Revista Medica de Chile 1991;119(4):402‐405. - PubMed
Pilmer 1993 {published data only}
-
- Pilmer BL, Green JA, Panacek EA, Elliot WJ, Murphy MB, Rutherford W, Nara AR. Fenoldopam mesylate versus sodium nitroprusside in the acute management of severe systemic hypertension. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1993;33(6):549‐553. - PubMed
Pujadas 1987 {published data only}
-
- Pujadas R, Jane J, Fornos C, Gago MJ, CN. Comparison of sublingual captopril and nifedipine in hypertensive crises. Archives of Internal Medicine 1987;147(1):175‐176. - PubMed
Reisin 1990 {published data only}
-
- Reisin E, Huth MM, Nguyen BP, Weed SG, Gonzalez FM. Intravenous fenoldopam versus sodium nitroprusside in patients with severe hypertension. Hypertension 1990;15(2 Suppl):I59‐I62. - PubMed
Risler 1998 {published data only}
-
- Risler T, Bohm R, Wetzchewald D, Nast HP, Koch HH, Stein G, Erley CM. A comparison of the antihypertensive efficacy and safety of felodipine IV and nifedipine IV in patients with hypertensive crisis or emergency not responding to oral nifedipine. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1998;54(4):295‐298. - PubMed
Rohr 1994 {published data only}
-
- Rohr G, Reimnitz P, Blanke P. Treatment of hypertensive emergency. Comparison of a new dosage form of the calcium antagonist nitrendipine with nifedipine capsules. Intensive Care Medicine 1994;20(4):268‐271. - PubMed
Spah 1988 {published data only}
-
- Spah F, Grosser KD. Treatment of hypertensive urgencies and emergencies with nitrendipine, nifedipine, and clonidine: effect on blood pressure and heart rate. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology 1988;12 Suppl 4:S154‐S156. - PubMed
Yoshida 1998 {published data only}
-
- Yoshida Noriko ea. Antihypertensive Effect of the Long‐Acting Ca Antagonist Amlodipine vs. Sustained‐Release Nifedipine in Patients with Acute Aortic Dissection. Rinsho to Kenkyu (The Japanese Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine) 1998;75(6):1419‐1422.
Zampaglione 1994 {published data only}
-
- Zampaglione B, Pascale C, Marchisio M, Santoro A. The use of lacidipine in the management of hypertensive crises: a comparative study with nifedipine. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology 1994;23 Suppl 5:S116‐S118. - PubMed
Additional references
Antman 2004
-
- Antman EM, Anbe DT, Armstrong PW, Bates ER, Green LA, Hand M, Hochman JS, Krumholz HM, Kushner FG, Lamas GA, Mullany CJ, Ornato JP, Pearle DL, Sloan MA, Smith SC, Jr, Alpert JS, Anderson JL, Faxon DP, Fuster V, Gibbons RJ, Gregoratos G, Halperin JL, Hiratzka LF, Hunt SA, Jacobs AK, American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, Canadian Cardiovascular Society. ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with ST‐elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee to Revise the 1999 Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction).[erratum appears in Circulation. 2005 Apr 19;111(15):2013‐4]. Circulation 2004;110(9):e82‐292. - PubMed
BASC 2001
-
- Blood pressure in Acute Stroke Collaboration (BASC). Interventions for deliberately altering blood pressure in acute stroke. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 2. - PubMed
Cherney 2002
Dalen 1979
-
- Dalen JE, Howe JP, III. Dissection of the aorta. Current diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. JAMA 1979;242(14):1530‐2. - PubMed
Duley 2006
-
- Duley L, Henderson‐Smart DJ, Meher S. Drugs for treatment of very high blood pressure during pregnancy.[update of Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006]. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 3. - PubMed
Gifford 1959
-
- Gifford RW. Treatment of Hypertensive Emergencies, including use of Sodium Nitroprusside. Mayo Clin Proc 1959;34(16):387. - PubMed
JNC‐7
-
- Chobanian, A.V, Bakris, G.L, Black, H.R, Cushman, W.C, Green, L.A, Izzo, J.L, Jr, Jones, D.W, Materson, B.J, Oparil, S, Wright, J.T, Jr, Roccella, E.J, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure, National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. JAMA 2003;289(19):2560‐2572. - PubMed
Krogsgaard 1983
-
- Krogsgaard, A.R, Hilden, T, McNair, A, Nielsen, P.E. Cerebral symptoms and blood pressure during parenteral administration of chlorpromazine, dihydralazine and diazoxide. Danish multicentre study on acute severe hypertension. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1983;Suppl 678:51‐60. - PubMed
Krogsgaard 1986‐D
-
- Krogsgaard AR, McNair A, Hilden T, Nielsen PE. Reversibility of cerebral symptoms in severe hypertension in relation to acute antihypertensive therapy.Danish Multicenter Study.. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1986;220(1):25‐31. - PubMed
Mattu 2005
-
- Mattu A, Martinez JP, Kelly BS. Modern management of cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America 2005;23(4):1105‐25. - PubMed
McNair 1985‐D
-
- McNair A, Krogsgaard AR, Hilden T, Nielsen PE. Reversibility of cerebral symptoms in severe hypertension in relation to acute antihypertensive therapy. Danish Multicenter study.. Acta medica Scandinavica.Supplementum. 1985;693:107‐110. - PubMed
McNair 1986
-
- McNair A, Krogsgaard AR, Hilden T, Nielsen PE. Severe hypertension with cerebral symptoms treated with furosemide, fractionated diazoxide or dihydralazine. Danish Multicenter Study. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1986;220(1):15‐23. - PubMed
Roberts 2004
-
- Roberts I, Yates D, Sandercock P, Farrell B, Wasserberg J, Lomas G, Cottingham R, Svoboda P, Brayley N, Mazairac G, Laloe V, Munoz‐Sanchez A, Arango M, Hartzenberg B, Khamis H, Yutthakasemsunt S, Komolafe E, Olldashi F, Yadav Y, Murillo‐Cabezas F, Shakur H, Edwards P, CRASH tc. Effect of intravenous corticosteroids on death within 14 days in 10008 adults with clinically significant head injury (MRC CRASH trial): randomised placebo‐controlled trial.[see comment]. Lancet 2004;364(9442):1321‐1328. - PubMed
Wilson 2005
-
- Wilson SR, Hirsch NP, Appleby I. Management of subarachnoid haemorrhage in a non‐neurosurgical centre. Anaesthesia 2005;60(5):470‐85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

