Extracellular purines are biomarkers of neutrophilic airway inflammation
- PMID: 18256064
- PMCID: PMC2723793
- DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00089807
Extracellular purines are biomarkers of neutrophilic airway inflammation
Abstract
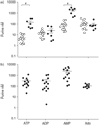
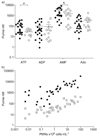
Purinergic signalling regulates airway defence mechanisms, suggesting that extracellular purines could serve as airway inflammation biomarkers in cystic fibrosis (CF). The purines adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP), adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and adenosine were measured in sputum from 21 adults (spontaneously expectorated from seven CF patients, induced from 14 healthy controls) to assess normal values and CF-associated changes. Subsequently, purine levels were measured in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from 37 children (25 CF patients, 12 disease controls) and compared with neutrophil counts, presence of airway infection and lung function. To noninvasively assess airway purines, ATP levels were measured using luminometry in exhaled breath condensate (EBC) from 14 children with CF and 14 healthy controls, then 14 CF children during a pulmonary exacerbation. Both ATP and AMP were elevated in sputum and BALF from CF subjects compared with controls. In BALF, ATP and AMP levels were inversely related to lung function and strongly correlated with neutrophil counts. In EBC, ATP levels were increased in CF relative to controls and decreased after treatment of CF pulmonary exacerbation. The purines adenosine triphosphate and adenosine monophosphate are candidate biomarkers of neutrophilic airways inflammation. Measurement of purines in sputum or exhaled breath condensate may provide a relatively simple and noninvasive method to track this inflammation.
Figures

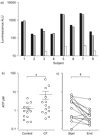
 ), compared with samples kept at 0°C on ice (■), and disappeared after incubation with 2 units·mL−1 of the ATP degrading enzyme apyrase (□). b) ATP levels were measured in EBC from CF (n=14) and healthy controls (n=14). ATP was elevated in the CF group. c) ATP levels in EBC were measured at the start and end of a course of antibiotics to treat a pulmonary exacerbation in children with CF (n=14). ATP levels were lower at the end of treatment. ALU: arbitrary light units. #: p=0.0441;¶: p=0.0175.
), compared with samples kept at 0°C on ice (■), and disappeared after incubation with 2 units·mL−1 of the ATP degrading enzyme apyrase (□). b) ATP levels were measured in EBC from CF (n=14) and healthy controls (n=14). ATP was elevated in the CF group. c) ATP levels in EBC were measured at the start and end of a course of antibiotics to treat a pulmonary exacerbation in children with CF (n=14). ATP levels were lower at the end of treatment. ALU: arbitrary light units. #: p=0.0441;¶: p=0.0175.Similar articles
-
Mass spectrometric analysis of biomarkers and dilution markers in exhaled breath condensate reveals elevated purines in asthma and cystic fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Jun;296(6):L987-93. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90512.2008. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19304910 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Exhaled breath condensate purines correlate with lung function in infants and preschoolers.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2013 Feb;48(2):182-7. doi: 10.1002/ppul.22573. Epub 2012 May 21. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2013. PMID: 22615171 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Evaluation of Neutrophilic Airway Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis.Chest. 2015 Aug;148(2):507-515. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-1800. Chest. 2015. PMID: 25611918 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive biomarkers of airway inflammation in cystic fibrosis.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2003 Nov;9(6):516-21. doi: 10.1097/00063198-200311000-00012. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2003. PMID: 14534405 Review.
-
Regulation of airway nucleotides in chronic lung diseases.Subcell Biochem. 2011;55:75-93. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-1217-1_4. Subcell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21560045 Review.
Cited by
-
The Non-Invasive Detection of Pulmonary Exacerbations in Disorders of Mucociliary Clearance with Breath Analysis: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Jun 7;13(12):3372. doi: 10.3390/jcm13123372. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38929901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of ATP in cough hypersensitivity syndrome: new targets for treatment.J Thorac Dis. 2020 May;12(5):2781-2790. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-cough-001. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 32642186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometric analysis of biomarkers and dilution markers in exhaled breath condensate reveals elevated purines in asthma and cystic fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Jun;296(6):L987-93. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90512.2008. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19304910 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Alterations in Nutrient Availability in the Lungs During Streptococcus pneumoniae-Induced Pneumonia.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 14:2025.07.14.664699. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.14.664699. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40791442 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Metabolomics Investigation Reveals Metabolite Mediators Associated with Acute Lung Injury and Repair in a Murine Model of Influenza Pneumonia.Sci Rep. 2016 May 18;6:26076. doi: 10.1038/srep26076. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27188343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burnstock G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev. 1972;24:509–581. - PubMed
-
- Dubyak GR, el-Moatassim C. Signal transduction via P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP and other nucleotides. Am J Physiol. 1993;265:C577–C606. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S, Ahmad A, McConville G, et al. Lung epithelial cells release ATP during ozone exposure: signaling for cell survival. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005;39:213–226. - PubMed
-
- Smith CP, Vemulakonda VM, Kiss S, Boone TB, Somogyi GT. Enhanced ATP release from rat bladder urothelium during chronic bladder inflammation: effect of botulinum toxin A. Neurochem Int. 2005;47:291–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
