Schizosaccharomyces pombe Pxl1 is a paxillin homologue that modulates Rho1 activity and participates in cytokinesis
- PMID: 18256290
- PMCID: PMC2291433
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-07-0718
Schizosaccharomyces pombe Pxl1 is a paxillin homologue that modulates Rho1 activity and participates in cytokinesis
Abstract
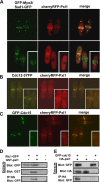
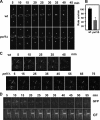
Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rho GTPases regulate actin cytoskeleton organization and cell integrity. We studied the fission yeast gene SPBC4F6.12 based on its ability to suppress the thermosensitivity of cdc42-1625 mutant strain. This gene, named pxl1(+), encodes a protein with three LIM domains that is similar to paxillin. Pxl1 does not interact with Cdc42 but it interacts with Rho1, and it negatively regulates this GTPase. Fission yeast Pxl1 forms a contractile ring in the cell division region and deletion of pxl1(+) causes a delay in cell-cell separation, suggesting that it has a function in cytokinesis. Pxl1 N-terminal region is required and sufficient for its localization to the medial ring, whereas the LIM domains are necessary for its function. Pxl1 localization requires actin polymerization and the actomyosin ring, but it is independent of the septation initiation network (SIN) function. Moreover, Pxl1 colocalizes and interacts with Myo2, and Cdc15, suggesting that it is part of the actomyosin ring. Here, we show that in cells lacking Pxl1, the myosin ring is not correctly assembled and that actomyosin ring contraction is delayed. Together, these data suggest that Pxl1 modulates Rho1 GTPase signaling and plays a role in the formation and contraction of the actomyosin ring during cytokinesis.
Figures

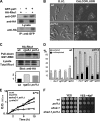
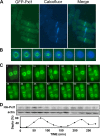
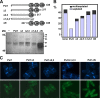
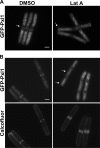

Comment in
- Mol Biol Cell. 19:1281.
References
-
- Arellano M., Coll P. M., Pérez P. Rho GTPases in the control of cell morphology, cell polarity, and actin localization in fission yeast. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1999a;47:51–60. - PubMed
-
- Arellano M., Duran A., Perez P. Localization of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rho1 GTPase and its involvement in the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. J. Cell Sci. 1997;110:2547–2555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

