State of hypertension management in the United States: confluence of risk factors and the prevalence of resistant hypertension
- PMID: 18256578
- PMCID: PMC8110159
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2008.07309.x
State of hypertension management in the United States: confluence of risk factors and the prevalence of resistant hypertension
Abstract
An improvement in the awareness and treatment of hypertension in the United States has occurred, resulting in the best control rates in the world, which unfortunately are far below the goals of Healthy People 2000 or 2010. This failure to achieve blood pressure (BP) goals is attributed to many factors, including an aging population, higher prevalence of kidney disease and obesity, high salt intake, physician inertia to increase dose and number of antihypertensive medications prescribed, and patient nonadherence with medication regimens. Resistant hypertension is defined as a failure to achieve goal BP in patients who adhere to full doses of an appropriate antihypertensive regimen of 3 drugs that includes a diuretic. The problem of resistant hypertension is projected to increase as the population ages. Efforts on the part of the Veterans Administration hospitals and others clearly indicate that a system can be implemented to help increase the percentage of persons in whom BP goal is achieved and reduce the prevalence of resistant hypertension. Medications specific to the problem of resistant hypertension are also under development. This review analyzes the status of hypertension control in the United States, the frequency of associated diseases, and adherence to guidelines; it further discusses strategies to reduce the prevalence of resistant hypertension.
Figures


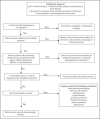
References
-
- Kaplan NM. Primary hypertension: pathogenesis. In: Kaplan NM, ed. Clinical Hypertension. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2002:56–135.
-
- The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High BP: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289(19):2560–2572. - PubMed
-
- Burt VL, Cutler JA, Higgins M, et al. Trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the adult US population. Data from the health examination surveys, 1960 to 1991. Hypertension. 1995;26(1):60–69. - PubMed
-
- Hajjar I, Kotchen TA. Trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the United States, 1988–2000. JAMA. 2003;290(2):199–206. - PubMed
-
- Ong KL, Cheung BM, Man YB, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among United States adults 1999–2004. Hypertension. 2007;49(1):69–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

