Combination therapy with Renin-Angiotensin-aldosterone receptor blockers for hypertension: how far have we come?
- PMID: 18256579
- PMCID: PMC8109960
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2008.07439.x
Combination therapy with Renin-Angiotensin-aldosterone receptor blockers for hypertension: how far have we come?
Abstract
In a large number of patients with hypertension, > or =2 antihypertensive agents are required to achieve blood pressure (BP) goals. There is good rationale for initial combination therapy based on clinical trials demonstrating that achievement of BP goals within a reasonably short period of time results in fewer cardiovascular events. One approach to attaining BP goals and improving medication adherence is fixed-dose combination therapy, the use of which dates back to the 1960s. Given some of the advantages of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) blockers in patients with heart disease, kidney disease, and diabetes, many combinations include either an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker. In most studies, however, thiazide diuretics were necessary to achieve goal BP. Calcium channel blockers have also been used in combination with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors to lower BP. Studies are now under way to determine the relative benefits of an RAAS blocker/diuretic compared with an RAAS blocker/calcium channel blocker as initial therapy.
Figures

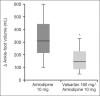
References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, et al. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42:1206–1252. - PubMed
-
- Epstein M, Bakris G. Newer approaches to antihypertensive therapy. Use of fixed‐dose combination therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:1969–1978. - PubMed
-
- Sica DA. Fixed‐dose combination antihypertensive drugs. Do they have a role in rational therapy? Drugs. 1994;48:16–24. - PubMed
-
- Sica DA. Rationale for fixed‐dose combinations in the treatment of hypertension: the cycle repeats. Drugs. 2002;62:443–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

