Cost-effectiveness of algorithms for confirmation test of human African trypanosomiasis
- PMID: 18257991
- PMCID: PMC2851529
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1310.060358
Cost-effectiveness of algorithms for confirmation test of human African trypanosomiasis
Abstract
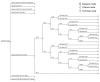
The control of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) is compromised by low sensitivity of the routinely used parasitologic confirmation tests. More sensitive alternatives, such as mini-anion exchange centrifugation technique (mAECT) or capillary tube centrifugation (CTC), are more expensive. We used formal decision analysis to assess the cost-effectiveness of alternative HAT confirmation algorithms in terms of cost per life saved. The effectiveness of the standard method, a combination of lymph node puncture (LNP), fresh blood examination (FBE), and thick blood film (TBF), was 36.8%; the LNP-FBE-CTC-mAECT sequence reached almost 80%. The cost per person examined ranged from euro1.56 for LNP-FBE-TBF to euro2.99 for LNP-TBF-CTC-mAECT-CATT (card agglutination test for trypanosomiasis) titration. LNP-TBF-CTC-mAECT was the most cost-effective in terms of cost per life saved. HAT confirmation algorithms that incorporate concentration techniques are more effective and efficient than the algorithms that are currently and routinely used by several T.b. gambiense control programs.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness): epidemiological update. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2006;81:69–80. - PubMed
-
- Miezan TW, Meda AH, Doua F, Cattand P. Evaluation of the parasitologic technics used in the diagnosis of human Trypanosoma gambiense trypanosomiasis in the Ivory Coast. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1994;87:101–4. - PubMed
-
- Paquet C, Castilla J, Mbulamberi D, Beaulieu MF, Gastellu Etchegorry MG, Moren A. Trypanosomiasis from Trypanosoma brucei gambiense in the center of north-west Uganda: evaluation of 5 years of control (1987–1991). Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 1995;88:38–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
