Emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus of animal origin in humans
- PMID: 18258032
- PMCID: PMC2876750
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1312.070384
Emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus of animal origin in humans
Abstract
In 2003 in the Netherlands, a new methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strain emerged that could not be typed with Sma1 pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (NT-MRSA). The association of NT-MRSA in humans with a reservoir in animals was investigated. The frequency of NT-MRSA increased from 0% in 2002 to >21% after intensified surveillance was implemented in July 2006. Geographically, NT-MRSA clustered with pig farming. A case-control study showed that carriers of NT-MRSA were more often pig or cattle farmers (pig farmers odds ratio [OR] 12.2, 95% confidence interval [CI] 3.1-48.6; cattle farmers OR 19.7, 95% CI 2.3-169.5). Molecular typing showed that the NT-MRSA strains belonged to a new clonal complex, ST 398. This study shows that MRSA from an animal reservoir has recently entered the human population and is now responsible for >20% of all MRSA in the Netherlands.
Figures
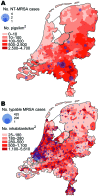
Comment in
-
SCCmec typing in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains of animal origin.Emerg Infect Dis. 2009 Jan;15(1):136-7; author reply 136-7. doi: 10.3201/eid1501.071647. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19116081 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
