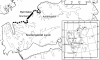
Spatial distribution of Echinococcus multilocularis, Svalbard, Norway
- PMID: 18258082
- PMCID: PMC2600161
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1401.070565
Spatial distribution of Echinococcus multilocularis, Svalbard, Norway
Abstract
In Svalbard, Norway, the only intermediate host for Echinococcus multilocularis, the sibling vole, has restricted spatial distribution. A survey of feces from the main host, the arctic fox, showed that only the area occupied by the intermediate host is associated with increased risk for human infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Echinococcus multilocularis in Svalbard, Norway: microsatellite genotyping to investigate the origin of a highly focal contamination.Infect Genet Evol. 2012 Aug;12(6):1270-4. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2012.03.008. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Infect Genet Evol. 2012. PMID: 22465539
-
On the move? Echinococcus multilocularis in red foxes of Saxony-Anhalt (Germany).Transbound Emerg Dis. 2014 Jun;61(3):239-46. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12026. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2014. PMID: 23134586
-
Fox faeces and vole distribution on a local range: ecological data in a parasitological perspective for Echinococcus multilocularis.Parasite. 2007 Dec;14(4):299-308. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2007144299. Parasite. 2007. PMID: 18225418
-
Mathematical modeling of Echinococcus multilocularis transmission.Parasitol Int. 2006;55 Suppl:S259-61. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2005.11.038. Epub 2005 Dec 15. Parasitol Int. 2006. PMID: 16343982 Review.
-
Wilderness in the city: the urbanization of Echinococcus multilocularis.Trends Parasitol. 2004 Feb;20(2):77-84. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2003.11.011. Trends Parasitol. 2004. PMID: 14747021 Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic review of the epidemiology of echinococcosis in domestic and wild animals.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013 Jun 6;7(6):e2249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002249. Print 2013. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013. PMID: 23755310 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation on the occurrence of Echinococcus multilocularis in Central Italy.BMC Vet Res. 2009 Nov 26;5:44. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-5-44. BMC Vet Res. 2009. PMID: 19941652 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal parasites of arctic foxes (Vulpes lagopus) and sibling voles (Microtus levis) in Spitsbergen, Svalbard.Parasitol Res. 2019 Dec;118(12):3409-3418. doi: 10.1007/s00436-019-06502-8. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Parasitol Res. 2019. PMID: 31729572
-
Westward spread of Echinococcus multilocularis in foxes, France, 2005-2010.Emerg Infect Dis. 2012 Dec;18(12):2059-62. doi: 10.3201/eid1812.120219. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 23171707 Free PMC article.
-
Multiscale ecological drivers of Echinococcus multilocularis spatial distribution in wild hosts: A systematic review.Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2023 Dec 2;34:e00216. doi: 10.1016/j.fawpar.2023.e00216. eCollection 2024 Mar. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 38152424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rausch RL. Life cycle patterns and geographic distribution of Echinococcus species. In: Thompson RCA, Lymbery AJ. Echinococcus and hydatid disease; 1995. Oxon (UK): CAB International. p. 89–134.
-
- Frafjord K, Prestrud P. Home range and movements of arctic foxes Alopex lagopus in Svalbard. Polar Biol. 1992;12:519–26.
-
- Jepsen JU, Eide NE, Prestrud P, Jacobsen LB. The importance of prey distribution in habitat use by arctic foxes (Alopex lagopus). Can J Zool. 2002;80:418–29. 10.1139/z02-023 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical