Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A in children, South Korea
- PMID: 18258121
- PMCID: PMC2600206
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1402.070807
Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A in children, South Korea
Abstract
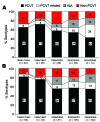
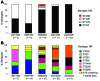
Despite the concern of replacement disease, notably by serotype 19A after 7-valent conjugate vaccine (PCV7) use, serotype 19A was increasingly recognized in Korean children before the introduction of PCV7. To understand the dynamics of serogroup 19 prevalence from 1991-2006, we serotyped 538 pediatric pneumococcal isolates. Serogroup 19 isolates (n = 126) were characterized by antimicrobial drug susceptibility, presence of mefA/ermB, and multilocus sequence typing. Overall, the proportion of serotype 19A isolates increased but serotype 19F decreased. Among children <5 years of age, the proportion of serotype 19A isolates in invasive pneumococcal disease increased from 0% in 1991-1994 to 8%-10% in 1995-2000, reached 26% in 2001-2003, and remained at 20% in 2004-2006 when vaccine coverage did not exceed 25% (p = 0.005 for trend). This study demonstrates that the expansion of multidrug-resistant ST320 was responsible for the increase in serotype 19A before PCV7 use.
Figures


References
-
- Black S, Shinefield H, Baxter R, Austrian R, Bracken L, Hansen J, et al. Postlicensure surveillance for pneumococcal invasive disease after use of heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Northern California Kaiser Permanente. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004;23:485–9. 10.1097/01.inf.0000129685.04847.94 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kaplan SL, Mason EO, Wald ER, Schutze GE, Bradley JS, Tan TO, et al. Decrease of invasive pneumococcal infections in children among 8 children’s hospitals in the United States after the introduction of the 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Pediatrics. 2004;113:443–9. 10.1542/peds.113.3.443 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
