Phenotypic and functional heterogeneity of human memory B cells
- PMID: 18258454
- PMCID: PMC2440717
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.12.006
Phenotypic and functional heterogeneity of human memory B cells
Abstract
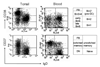
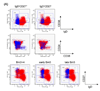
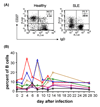
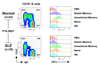
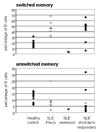
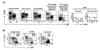
Memory B cells are more heterogeneous than previously thought. Given that B cells play powerful antibody-independent effector functions, it seems reasonable to assume division of labor between distinct memory B cells subpopulations in both protective and pathogenic immune responses. Here we review the information emerging regarding the heterogeneity of human memory B cells. A better understanding of this topic should greatly improve our ability to target specific B cell subsets either in vaccine responses or in autoimmune diseases and organ rejection among other pathological conditions where B cells play central pathogenic roles.
Figures


References
-
- Sallusto F, Geginat J, Lanzavecchia A. Central Memory and Effector Memory T Cell Subsets: Function, Generation, and Maintenance. Annual Review of Immunology. 2004;22:745–763. - PubMed
-
- Ochsenbein AF, Pinschewer DD, Sierro S, Horvath E, Hengartner H, Zinkernagel RM. Protective long-term antibody memory by antigen-driven and T help-dependent differentiation of long-lived memory B cells to short-lived plasma cells independent of secondary lymphoid organs. PNAS. 2000;97:13263–13268. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Slifka MK, Antia R, Whitmire JK, Ahmed R. Humoral Immunity Due to Long-Lived Plasma Cells. Immunity. 1998;8:363–372. - PubMed
-
- Martin F, Chan AC. B Cell Immunobiology in Disease: Evolving Concepts from the Clinic. Annual Review of Immunology. 2006;24 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

