Biology of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha in development and disease
- PMID: 18259197
- PMCID: PMC2882207
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2008.17
Biology of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha in development and disease
Abstract
The transcriptional response to hypoxia is primarily mediated by two hypoxia-inducible factors--HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha. While these proteins are highly homologous, increasing evidence suggests they have unique transcriptional targets and differential impact on tumor growth. Furthermore, non-transcriptional effects of the HIF-alpha subunits, including effects on the Notch and c-Myc pathways, contribute to their distinct functions. HIF-2alpha transcriptional targets include genes involved in erythropoiesis, angiogenesis, metastasis, and proliferation. Therefore, HIF-2alpha contributes significantly to both normal physiology as well as tumorigenesis. Here, we summarize the function of HIF-2alpha during development as well as its contribution to pathologic conditions, such as tumors and vascular disease.
Figures
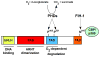

References
-
- Harris AL. Hypoxia--a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:38–47. - PubMed
-
- Covello KL, Simon MC. HIFs, hypoxia, and vascular development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2004;62:37–54. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science. 2005;307:58–62. - PubMed
-
- Gu YZ, Hogenesch JB, Bradfield CA. The PAS superfamily: sensors of environmental and developmental signals. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2000;40:519–61. - PubMed
-
- Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, et al. Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science. 2001;292:468–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

