Idiopathic benign retroperitoneal cyst: a case report
- PMID: 18261209
- PMCID: PMC2262907
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-2-43
Idiopathic benign retroperitoneal cyst: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Retroperitoneal cysts are uncommon, with an estimated incidence of 1/5750 to 1/250,000.
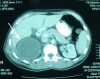
Case presentation: A male patient was admitted with an abdominal pain, jaundice and fever. Clinical examination and investigations confirmed an idiopathic benign retroperitoneal cyst. He underwent surgery and was discharged after making good recovery.
Conclusion: Retroperitoneal cysts are very rare, and most of the time they are discovered incidentally. Patients may be asymptomatic or present with abdominal pain, referred pain to the legs or weight loss. Imaging may help diagnose these lesions, but surgery is the keystone in confirming the diagnosis. This case is very rare and very educational as it highlights an unusual presentation of a benign retroperitoneal cyst. In our patient, the course of the disease was unique as the patient presented with jaundice.
Figures
References
-
- Guile M, Fagan M, Simopolous A, Ellerkman M. Retroperitoneal Cyst of Mullerian Origin: A case report and review of the literature. J of Pelvic Medicine and Surgery. 2007;13:149–152. doi: 10.1097/SPV.0b013e3180622272. - DOI
-
- Handfield-Jones R. Retroperitoneal Cysts: Their Pathology, Diagnosis and Treatment. BJS. 1942. pp. 119–134.
-
- Felix EdwardL, Wood DonaldK, Das Gupta TapasK. Tumours of the Retroperitoneun. Cancer. 1981;6:1–47. - PubMed
-
- Yang D, Jung D, Kim H, Kang H, Kim S, Kim J, Hwang H. Retroperitoneal cystic masses: CT, Clinical and Pathological Findings and Literature Review. RG. 2004;25:1353–1365. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources