Trypanosome H2Bv replaces H2B in nucleosomes enriched for H3 K4 and K76 trimethylation
- PMID: 18261990
- PMCID: PMC2276873
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.01.144
Trypanosome H2Bv replaces H2B in nucleosomes enriched for H3 K4 and K76 trimethylation
Abstract
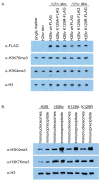
Some inroads have been made into characterizing histone variants and post translational modifications of histones in Trypanosoma brucei. Histone variant H2BV lysine 129 is homologous to Saccharomyces cerevisiae H2B lysine 123, whose ubiquitination is required for methylation of H3 lysines 4 and 79. We show that T. brucei H2BV K129 is not ubiquitinated, but trimethylation of H3 K4 and K76, homologs of H3 K4 and K79 in yeast, was enriched in nucleosomes containing H2BV. Mutation of H2BV K129 to alanine or arginine did not disrupt H3 K4 or K76 methylation. These data suggest that H3 K4 and K76 methylation in trypanosomes is regulated by a novel mechanism, possibly involving the replacement of H2B with H2BV in the nucleosome.
Figures



References
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Fischle W, Wang Y, Allis CD. Histone and chromatin cross-talk. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:172–83. - PubMed
-
- Briggs SD, Xiao T, Sun ZW, Caldwell JA, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Allis CD, Strahl BD. Gene silencing: trans-histone regulatory pathway in chromatin. Nature. 2002;418:498. - PubMed
-
- Sun ZW, Allis CD. Ubiquitination of histone H2B regulates H3 methylation and gene silencing in yeast. Nature. 2002;418:104–8. - PubMed
-
- Shilatifard A. Chromatin modifications by methylation and ubiquitination: implications in the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:243–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

