Coordinated expression of microRNA-155 and predicted target genes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 18262046
- PMCID: PMC2276854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2007.10.008
Coordinated expression of microRNA-155 and predicted target genes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
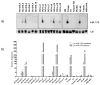
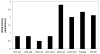
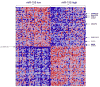
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) attenuate gene expression by pairing to the 3'UTR of target transcripts inducing RNA cleavage or translational inhibition. Overexpression of microRNA-155 (miR-155), measured either at the primary (BIC gene) or mature transcript level, was recently described in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL). These studies have been limited in size, however, and have not attempted to link miR-155 expression to that of putative target genes. To start to address these issues, we examined a collection of 22 well-characterized DLBCL cell lines. The expression of miR-155 is heterogeneous in these cell lines and associates with NF-kappaB activity. We found that the expression of the primary miR-155 transcript reliably reflects that of the functional mature miR-155. Because many gene array platforms include probe sets for the primary miR-155 sequences, these findings allowed us to confidently examine large array-based expression datasets of primary DLBCLs in the context of miR-155 levels. Our investigation revealed that miR-155 expression segregates with specific molecular subgroups of DLBCL and it is highest in activated B-cell (ABC)-type lymphomas. These tumors are characterized by constitutive activation of NF-kappaB signals, which supports the data derived from our cell lines. More importantly, using supervised learning algorithms, we identified a robust gene signature driven by the differential expression of miR-155. These profiles contained several gene markers, including predicted targets, consistently downregulated in tumors expressing high levels of miR-155. Our data start to unveil the genome-wide effects of miR-155 expression in DLBCL and indicate the utility of this strategy in the identification and validation of miRNA target genes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Infection of Cell Lines Derived from Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas Alters MicroRNA Loading of the Ago2 Complex.J Virol. 2019 Jan 17;93(3):e01297-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01297-18. Print 2019 Feb 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30429351 Free PMC article.
-
BIC and miR-155 are highly expressed in Hodgkin, primary mediastinal and diffuse large B cell lymphomas.J Pathol. 2005 Oct;207(2):243-9. doi: 10.1002/path.1825. J Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16041695
-
miR-181a negatively regulates NF-κB signaling and affects activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma pathogenesis.Blood. 2016 Jun 9;127(23):2856-66. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-11-680462. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Blood. 2016. PMID: 26941399
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Role of microRNA deregulation in the pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).Leuk Res. 2013 Nov;37(11):1420-8. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2013.08.020. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Leuk Res. 2013. PMID: 24054860 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-21 plays an oncogenic role by targeting FOXO1 and activating the PI3K/AKT pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 20;6(17):15035-49. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3729. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25909227 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori γ-glutamyl transpeptidase: a formidable virulence factor.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Dec 7;19(45):8203-10. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8203. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24363510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential micro-RNA expression in primary CNS and nodal diffuse large B-cell lymphomas.Neuro Oncol. 2011 Oct;13(10):1090-8. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nor107. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Neuro Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21803762 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of bromodomain proteins for the treatment of human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Jan 1;21(1):113-22. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3346. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25009295 Free PMC article.
-
Transfection of microRNA Mimics Should Be Used with Caution.Front Genet. 2015 Dec 2;6:340. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00340. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 26697058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
-
- Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–69. - PubMed
-
- Metzler M, Wilda M, Busch K, Viehmann S, Borkhardt A. High expression of precursor microRNA-155/BIC RNA in children with Burkitt lymphoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2004;39:167–9. - PubMed
-
- van den Berg A, Kroesen BJ, Kooistra K, de Jong D, Briggs J, Blokzijl T, Jacobs S, Kluiver J, Diepstra A, Maggio E, Poppema S. High expression of B-cell receptor inducible gene BIC in all subtypes of Hodgkin lymphoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2003;37:20–8. - PubMed
-
- Kluiver J, Poppema S, de Jong D, Blokzijl T, Harms G, Jacobs S, Kroesen BJ, van den Berg A. BIC and miR-155 are highly expressed in Hodgkin, primary mediastinal and diffuse large B cell lymphomas. J Pathol. 2005;207:243–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

