Acetamido sugar biosynthesis in the Euryarchaea
- PMID: 18263721
- PMCID: PMC2293230
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01970-07
Acetamido sugar biosynthesis in the Euryarchaea
Abstract
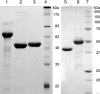
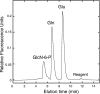
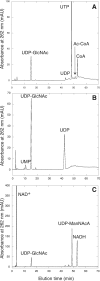
Archaea and eukaryotes share a dolichol phosphate-dependent system for protein N-glycosylation. In both domains, the acetamido sugar N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) forms part of the core oligosaccharide. However, the archaeal Methanococcales produce GlcNAc using the bacterial biosynthetic pathway. Key enzymes in this pathway belong to large families of proteins with diverse functions; therefore, the archaeal enzymes could not be identified solely using comparative sequence analysis. Genes encoding acetamido sugar-biosynthetic proteins were identified in Methanococcus maripaludis using phylogenetic and gene cluster analyses. Proteins expressed in Escherichia coli were purified and assayed for the predicted activities. The MMP1680 protein encodes a universally conserved glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase. The MMP1077 phosphomutase converted alpha-D-glucosamine-6-phosphate to alpha-D-glucosamine-1-phosphate, although this protein is more closely related to archaeal pentose and glucose phosphomutases than to bacterial glucosamine phosphomutases. The thermostable MJ1101 protein catalyzed both the acetylation of glucosamine-1-phosphate and the uridylyltransferase reaction with UTP to produce UDP-GlcNAc. The MMP0705 protein catalyzed the C-2 epimerization of UDP-GlcNAc, and the MMP0706 protein used NAD(+) to oxidize UDP-N-acetylmannosamine, forming UDP-N-acetylmannosaminuronate (ManNAcA). These two proteins are similar to enzymes used for proteobacterial lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis and gram-positive bacterial capsule production, suggesting a common evolutionary origin and a widespread distribution of ManNAcA. UDP-GlcNAc and UDP-ManNAcA biosynthesis evolved early in the euryarchaeal lineage, because most of their genomes contain orthologs of the five genes characterized here. These UDP-acetamido sugars are predicted to be precursors for flagellin and S-layer protein modifications and for the biosynthesis of methanogenic coenzyme B.
Figures
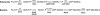

Similar articles
-
Identification of a Direct Biosynthetic Pathway for UDP-N-Acetylgalactosamine from Glucosamine-6-Phosphate in Thermophilic Crenarchaeon Sulfolobus tokodaii.J Bacteriol. 2018 Apr 24;200(10):e00048-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00048-18. Print 2018 May 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29507091 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient chemoenzymatic synthesis of uridine 5'-diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine and uridine 5'-diphosphate N-trifluoacetyl glucosamine with three recombinant enzymes.Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2017 Oct 21;47(9):852-859. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2016.1188315. Epub 2016 May 24. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27220687
-
Hexosamine biosynthesis in keratinocytes: roles of GFAT and GNPDA enzymes in the maintenance of UDP-GlcNAc content and hyaluronan synthesis.Glycobiology. 2016 Jul;26(7):710-22. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cww019. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Glycobiology. 2016. PMID: 26887390
-
Enzymes of UDP-GlcNAc biosynthesis in yeast.Yeast. 2006 Jan 15;23(1):1-14. doi: 10.1002/yea.1337. Yeast. 2006. PMID: 16408321 Review.
-
Highlights of glucosamine-6P synthase catalysis.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008 Jun 15;474(2):302-17. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.01.026. Epub 2008 Feb 6. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008. PMID: 18279655 Review.
Cited by
-
AglC and AglK are involved in biosynthesis and attachment of diacetylated glucuronic acid to the N-glycan in Methanococcus voltae.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jan;191(1):187-95. doi: 10.1128/JB.00885-08. Epub 2008 Oct 31. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 18978056 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that biosynthesis of the second and third sugars of the archaellin Tetrasaccharide in the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis occurs by the same pathway used by Pseudomonas aeruginosa to make a di-N-acetylated sugar.J Bacteriol. 2015 May;197(9):1668-80. doi: 10.1128/JB.00040-15. Epub 2015 Mar 2. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25733616 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of Geobacter metallireducens: features of metabolism, physiology and regulation common and dissimilar to Geobacter sulfurreducens.BMC Microbiol. 2009 May 27;9:109. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-109. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19473543 Free PMC article.
-
N-linked glycosylation in Archaea: a structural, functional, and genetic analysis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014 Jun;78(2):304-41. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00052-13. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24847024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a putative acetyltransferase gene, MMP0350, which affects proper assembly of both flagella and pili in the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis.J Bacteriol. 2008 Aug;190(15):5300-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.00474-08. Epub 2008 Jun 6. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18539748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu-Qarn, M., and J. Eichler. 2006. Protein N-glycosylation in Archaea: defining Haloferax volcanii genes involved in S-layer glycoprotein glycosylation. Mol. Microbiol. 61511-525. - PubMed
-
- Akutsu, J.-I., Z. Zhang, M. Tsujimura, M. Sasaki, M. Yohda, and Y. Kawarabayasi. 2005. Characterization of a thermostable enzyme with phosphomannomutase/phosphoglucomutase activities from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3. J. Biochem. 138159-166. - PubMed
-
- Bult, C. J., O. White, G. J. Olsen, L. Zhou, R. D. Fleischmann, G. G. Sutton, J. A. Blake, L. M. FitzGerald, R. A. Clayton, J. D. Gocayne, A. R. Kerlavage, B. A. Dougherty, J.-F. Tomb, M. D. Adams, C. I. Reich, R. Overbeek, E. F. Kirkness, K. G. Weinstock, J. M. Merrick, A. Glodek, J. L. Scott, N. S. M. Geoghagen, H. O. Smith, C. R. Woese, and J. C. Venter. 1996. Complete genome sequence of the methanogenic archaeon, Methanococcus jannaschii. Science 2731017-1140. - PubMed
-
- Burda, P., and M. Aebi. 1999. The dolichol pathway of N-linked glycosylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1426239-257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

