BDNF is essential to promote persistence of long-term memory storage
- PMID: 18263738
- PMCID: PMC2268201
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0711863105
BDNF is essential to promote persistence of long-term memory storage
Abstract
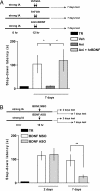
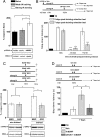
Persistence is a characteristic attribute of long-term memories (LTMs). However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms that mediate this process. We recently showed that persistence of LTM requires a late protein synthesis- and BDNF-dependent phase in the hippocampus. Here, we show that intrahippocampal delivery of BDNF reverses the deficit in memory persistence caused by inhibition of hippocampal protein synthesis. Importantly, we demonstrate that BDNF induces memory persistence by itself, transforming a nonlasting LTM trace into a persistent one in an ERK-dependent manner. Thus, BDNF is not only necessary, but sufficient to induce a late postacquisition phase in the hippocampus essential for persistence of LTM storage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bailey CH, Kandel ER, Si K. The persistence of long-term memory: A molecular approach to self-sustaining changes in learning-induced synaptic growth. Neuron. 2004;44:49–57. - PubMed
-
- McGaugh JL. Memory—a century of consolidation. Science. 2000;287:248–251. - PubMed
-
- Lamprecht R, LeDoux J. Structural plasticity and memory. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:45–54. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Ferguson GD, Pineda VV, Cundiff PE, Storm DR. Overexpression of type-1 adenylyl cyclase in mouse forebrain enhances recognition memory and LTP. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:635–642. - PubMed
-
- Han JH, et al. Neuronal competition and selection during memory formation. Science. 2007;316:457–460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

