Human Pso4 is a metnase (SETMAR)-binding partner that regulates metnase function in DNA repair
- PMID: 18263876
- PMCID: PMC2431028
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M800150200
Human Pso4 is a metnase (SETMAR)-binding partner that regulates metnase function in DNA repair
Abstract
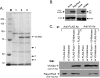
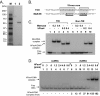
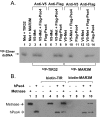
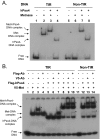
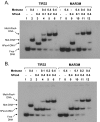
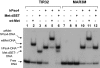
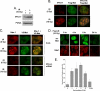
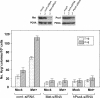
Metnase, also known as SETMAR, is a SET and transposase fusion protein with an undefined role in mammalian DNA repair. The SET domain is responsible for histone lysine methyltransferase activity at histone 3 K4 and K36, whereas the transposase domain possesses 5'-terminal inverted repeat (TIR)-specific DNA binding, DNA looping, and DNA cleavage activities. Although the transposase domain is essential for Metnase function in DNA repair, it is not clear how a protein with sequence-specific DNA binding activity plays a role in DNA repair. Here, we show that human homolog of the ScPSO4/PRP19 (hPso4) forms a stable complex with Metnase on both TIR and non-TIR DNA. The transposase domain essential for Metnase-TIR interaction is not sufficient for its interaction with non-TIR DNA in the presence of hPso4. In vivo, hPso4 is induced and co-localized with Metnase following ionizing radiation treatment. Cells treated with hPso4-siRNA failed to show Metnase localization at DSB sites and Metnase-mediated stimulation of DNA end joining coupled to genomic integration, suggesting that hPso4 is necessary to bring Metnase to the DSB sites for its function(s) in DNA repair.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Metnase's TIR binding activity by its binding partner, Pso4.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010 Jun 15;498(2):89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.04.011. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010. PMID: 20416268 Free PMC article.
-
Metnase/SETMAR: a domesticated primate transposase that enhances DNA repair, replication, and decatenation.Genetica. 2010 May;138(5):559-66. doi: 10.1007/s10709-010-9452-1. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Genetica. 2010. PMID: 20309721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human set and transposase domain protein Metnase interacts with DNA Ligase IV and enhances the efficiency and accuracy of non-homologous end-joining.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Dec 1;7(12):1927-37. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.08.002. Epub 2008 Sep 18. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18773976 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical characterization of a SET and transposase fusion protein, Metnase: its DNA binding and DNA cleavage activity.Biochemistry. 2007 Oct 9;46(40):11369-76. doi: 10.1021/bi7005477. Epub 2007 Sep 18. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17877369 Free PMC article.
-
hPso4/hPrp19: a critical component of DNA repair and DNA damage checkpoint complexes.Oncogene. 2016 May 5;35(18):2279-86. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.321. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26364595 Review.
Cited by
-
Metnase and EEPD1: DNA Repair Functions and Potential Targets in Cancer Therapy.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 28;12:808757. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.808757. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35155245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA damage induces down-regulation of Prp19 via impairing Prp19 stability in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 28;9(2):e89976. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089976. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587161 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic Transport Machinery of the SPF27 Homologue Num1 in Ustilago maydis.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 26;8(1):3611. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21628-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29483520 Free PMC article.
-
A Proteomic Strategy Identifies Lysine Methylation of Splicing Factor snRNP70 by the SETMAR Enzyme.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 8;290(19):12040-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.641530. Epub 2015 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25795785 Free PMC article.
-
The function of the NineTeen Complex (NTC) in regulating spliceosome conformations and fidelity during pre-mRNA splicing.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Aug;38(4):1110-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0381110. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20659013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hamamoto, R., Furukawa, Y., Morita, M., Iimura, Y., Silva, F. P., Li, M., Yagyu, R., and Nakamura, Y. (2004) Nat. Cell Biol. 6 731-740 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

