Involvement of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin-induced plasma extravasation in mice
- PMID: 18264118
- PMCID: PMC2275440
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.9
Involvement of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin-induced plasma extravasation in mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin, an important agent of necrotic enteritis, causes plasma extravasation due to the release of a tachykinin NK(1) receptor agonist in mouse skin. In this study, we investigated the role of cytokines in beta-toxin-induced plasma extravasation.
Experimental approach: Male Balb/c, C3H/HeN and C3H/HeJ mice were anaesthetized with pentobarbitone and beta-toxin was injected i.d. into shaved dorsal skin. SR140333, capsaicin, chlorpromazine and pentoxifylline were given as pretreatment when required before the injection of the toxin. Cytokines in the dorsal skin were measured by ELISA.
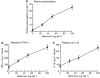
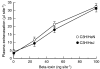
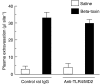
Key results: Injection (i.d.) of beta-toxin induced a dose-dependent increase in dermal TNF-alpha and interleukin (IL)-1beta levels with a concomitant increase in plasma extravasation, but not the release of IL-6. SR140333 and capsaicin significantly inhibited the toxin-induced release of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. The plasma extravasation and the release of TNF-alpha induced by beta-toxin were significantly inhibited by chlorpromazine and pentoxifylline which inhibit the release of TNF-alpha. The toxin-induced plasma extravasation in mouse skin was attenuated by pretreatment with a monoclonal antibody against TNF-alpha, but not anti-IL-1beta. Furthermore, the toxin caused an increase in plasma extravasation in both C3H/HeN (TLR4-intact) and C3H/HeJ (TLR4-deficient) mice. In C3H/HeN mice, the toxin-induced leakage was not inhibited by pretreatment with anti-TLR4/MD-2 antibody.
Conclusions and implications: These observations show that beta-toxin-induced plasma extravasation in mouse skin is related to the release of TNF-alpha via the mechanism involving tachykinin NK(1) receptors, but not via TLR4.
Figures
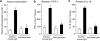

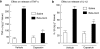

Similar articles
-
Involvement of tachykinin receptors in Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin-induced plasma extravasation.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Jan;138(1):23-30. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705022. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12522069 Free PMC article.
-
The antiinflammatory effects of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction on C3H/HeJ mice with alopecia areata.Phytomedicine. 2021 Jan;81:153423. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153423. Epub 2020 Nov 22. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33310308
-
Toll-Like Receptor 4 Protects Against Clostridium perfringens Infection in Mice.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Mar 8;11:633440. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.633440. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33763386 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Survival and Neurological Outcomes after Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Toll-like Receptor 4-mutant Mice.Chin Med J (Engl). 2015 Oct 5;128(19):2646-51. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.166024. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015. PMID: 26415804 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental photoaging in C3H/HeN, C3H/HeJ, and Balb/c mice: comparison of changes in extracellular matrix components and mast cell numbers.J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Dec;103(6):797-800. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12413286. J Invest Dermatol. 1994. PMID: 7798617
Cited by
-
Recent insights into Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Feb 3;7(2):396-406. doi: 10.3390/toxins7020396. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25654787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Berberine on Intestinal Morphology, Microbes, and Immune Function of Broilers in Response to Necrotic Enteritis Challenge.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Oct 19;2021:1877075. doi: 10.1155/2021/1877075. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34712727 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in understanding the pathogenesis of Clostridium perfringens type C infections.Vet Microbiol. 2011 Nov 21;153(1-2):37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.02.048. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Vet Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21420802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Trends on Mitigative Effect of Probiotics on Oxidative-Stress-Induced Gut Dysfunction in Broilers under Necrotic Enteritis Challenge: A Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Apr 11;12(4):911. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040911. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clostridium Perfringens Toxins Involved in Mammalian Veterinary Diseases.Open Toxinology J. 2010;2:24-42. Open Toxinology J. 2010. PMID: 24511335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akashi S, Shimazu R, Ogata H, Nagai Y, Takeda K, Kimoto M, et al. Cutting edge: cell surface expression and lipopolysaccharide signaling via the toll-like receptor 4-MD-2 complex on mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 2000;164:3471–3475. - PubMed
-
- Alber G, Scheuber PH, Reck B, Sailer-Kramer B, Hartmann A, Hammer DK. Role of substance P in immediate-type skin reactions induced by staphylococcal enterotoxin B in unsensitized monkeys. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989;84:880–885. - PubMed
-
- Ansel JC, Armstrong CA, Song I, Quinlan KL, Olerud JE, Caughman SW, et al. Interactions of the skin and nervous system. J Invest Dermatol Symp Proc. 1997;2:23–26. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B. Inferences, questions and possibilities in toll-like receptor signalling. Nature. 2004;430:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Chaves F, Teixeira CFP, Gutiérrez JM. Role of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in the local tissue damage induced by Bothrops asper snake venom: an experimental assessment in mice. Toxicon. 2005;45:171–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

