ER alpha negative breast cancer cells restore response to endocrine therapy by combination treatment with both HDAC inhibitor and DNMT inhibitor
- PMID: 18264725
- PMCID: PMC12160743
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-008-0354-x
ER alpha negative breast cancer cells restore response to endocrine therapy by combination treatment with both HDAC inhibitor and DNMT inhibitor
Abstract
Purpose: Estrogen receptor alpha (ER alpha) mediates the growth stimulation of estrogen in breast cancer cells and is a useful predictive factor for response to endocrine therapy. It is reported that ER alpha was induced in ER alpha negative breast cancer cells by both DNA methyltransferase-1 (DNMT1) inhibitor 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (AZA) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA). However, whether the breast cancer cells with induced ER alpha restore response to endocrine therapy requires to be further researched.
Patients and methods: Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method was used to explore the change in the mRNA of ER alpha, PR and pS2 in the ER alpha negative breast cancer cells MDA-MB-435 treated with two chemicals (AZA + TSA). Water-soluble tetrazolium salt-8 (WST-8) method was used to study the proliferation rate of the breast cancer cells. Flow cytometer (FCW) was used to analyze the distribution of cell cycle of these breast cancer cells. Some xenograft models in nude mice were used to further study the results we found in vitro.
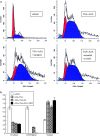
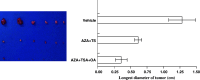
Results: In this study we observed that the mRNA of ER alpha, PR and pS2 in the ER alpha negative breast cancer cells MDA-MB-435 was re-expressed by treatment with AZA + TSA. The proliferation assay analysis showed AZA + TSA suppressed the proliferation of MDA-MB-435 cells, which were further suppressed by addition of 4-OH Tamoxifen (4-OHT). On the contrary, the proliferation of cells treated with 4-OHT alone showed no difference compared with the vehicle control. Cell cycle analysis showed AZA + TSA treated cells showed S phase arrest, which was partially attenuated by addition of estradiol (E2); furthermore, the effect of E2 on stimulation of cell cycle could be reversed by 4-OHT in the treated cells with induced ER alpha. In vivo experiment xenograft volume of MDA-MB-435 cells treated with AZA + TSA was smaller than that of the control (P < 0.01), and the xenograft of AZA + TSA treated cells was further suppressed by ovariectomy (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: Our data indicate that DNMT1 inhibitor AZA and HDAC inhibitor TSA play important roles in restoring sensitivity of the ER alpha negative breast cancer cells to endocrine therapy in vitro and in vivo.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Expression of ER alpha in chemically induced MDA-MB-435 cells and its responsiveness to endocrine].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2006 Dec;28(12):886-9. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17533736 Chinese.
-
Targeting tumour re-wiring by triple blockade of mTORC1, epidermal growth factor, and oestrogen receptor signalling pathways in endocrine-resistant breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2018 Jun 8;20(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13058-018-0983-1. Breast Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29880014 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic activation of functional estrogen receptor (ER)-alpha by DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibition in human ER-alpha-negative breast cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2001 Oct 1;61(19):7025-9. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11585728
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Mammographic density, endocrine therapy and breast cancer risk: a prognostic and predictive biomarker review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 26;10(10):CD013091. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013091.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34697802 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Gefitinib-mediated reversal of tamoxifen resistance in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by inducing ERα re-expression.Sci Rep. 2015 Feb 3;5:7835. doi: 10.1038/srep07835. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25644501 Free PMC article.
-
Positive Regulation of Estrogen Receptor Alpha in Breast Tumorigenesis.Cells. 2021 Oct 31;10(11):2966. doi: 10.3390/cells10112966. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Addition of a histone deacetylase inhibitor redirects tamoxifen-treated breast cancer cells into apoptosis, which is opposed by the induction of autophagy.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Nov;130(2):437-47. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1364-y. Epub 2011 Feb 5. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 21298336 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics in breast and prostate cancer.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1238:425-66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1804-1_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25421674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A prismatic view of the epigenetic-metabolic regulatory axis in breast cancer therapy resistance.Oncogene. 2024 Jun;43(23):1727-1741. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03054-9. Epub 2024 May 8. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38719949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baylin S, Bestor TH (2002) Altered methylation patterns in cancer cell genomes: cause or consequence? Cancer Cell 1(4):299–305 - PubMed
-
- Bovenzi V, Momparler RL (2001) Antineoplastic action of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine and histone deacetylase inhibitor and their effect on the expression of retinoic acid receptor beta and estrogen receptor alpha genes in breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 48(1):71–76 - PubMed
-
- Butler LM, Agus DB, Scher HI, Higgins B, Rose A, Cordon-Cardo C, Thaler HT, Rifkind RA, Marks PA, Richon VM (2000) Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, an inhibitor of histone deacetylase, suppresses the growth of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 60(18):5165–5170 - PubMed
-
- Cameron EE, Bachman KE, Myohanen S, Herman JG, Baylin SB (1999) Synergy of demethylation and histone deacetylase inhibition in the re-expression of genes silenced in cancer. Nat Genet 21(1):103–107 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

