Case report : femoral shaft fracture resulting from femoral tracker placement in navigated TKA
- PMID: 18264838
- PMCID: PMC2384040
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-008-0150-6
Case report : femoral shaft fracture resulting from femoral tracker placement in navigated TKA
Abstract
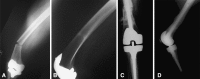
Computer-assisted navigation is a surgical tool that may decrease malalignment outliers in TKA. With any new surgical technique, there is the possibility of unexpected complications that raise caution. We report two patients with displaced femoral fractures at optical tracker pin placement sites created for routine performance of navigated TKA. Our experience suggests single bicortical 5-mm pins placed in the femoral shaft have the added risk of creating a stress riser leading to the potential for fracture. Females may have a higher risk for this complication. We believe bicortical pin fixation in the femur or tibia no longer is indicated.
Figures

References
-
- Brooks DB, Burstein AH, Frankel VH. The biomechanics of torsional fractures: the stress concentration effect of a drill hole. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970;52:507–514. - PubMed
-
- Burstein AH, Currey J, Frankel VH, Heiple JG, Lunseth P, Vessely JC. Bone strength: the effect of screw holes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972;54:1143–1156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

