X chromosome activity in mouse XX primordial germ cells
- PMID: 18266475
- PMCID: PMC2233679
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0040030
X chromosome activity in mouse XX primordial germ cells
Abstract
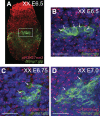
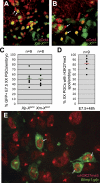
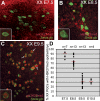
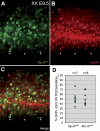
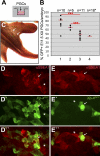
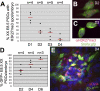
In the early epiblast of female mice, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly inactivated by a Xist-dependent mechanism, involving the recruitment of Ezh2-Eed and the subsequent trimethylation of histone 3 on lysine 27 (H3K27me3). We demonstrate that this random inactivation process applies also to the primordial germ cell (PGC) precursors, located in the proximal region of the epiblast. PGC specification occurs at about embryonic day (E)7.5, in the extraembryonic mesoderm, after which the germ cells enter the endoderm of the invaginating hindgut. As they migrate towards the site of the future gonads, the XX PGCs gradually lose the H3K27me3 accumulation on the silent X chromosome. However, using a GFP transgene inserted into the X chromosome, we observed that the XX gonadal environment (independently of the gender) is important for the substantial reactivation of the inactive X chromosome between E11.5 and E13.5, but is not required for X-chromosome reactivation during the derivation of pluripotent embryonic germ cells. We describe in detail one of the key events during female PGC development, the epigenetic reprogramming of the X chromosome, and demonstrate the role of the XX somatic genital ridge in this process.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Mak W, Nesterova TB, de Napoles M, Appanah R, Yamanaka S, et al. Reactivation of the paternal X chromosome in early mouse embryos. Science. 2004;303:666–669. - PubMed
-
- Okamoto I, Otte AP, Allis CD, Reinberg D, Heard E. Epigenetic dynamics of imprinted X inactivation during early mouse development. Science. 2004;303:644–649. - PubMed
-
- Rastan S. Timing of X-chromosome inactivation in postimplantation mouse embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1982;71:11–24. - PubMed
-
- Rastan S, Kaufman MH, Handyside AH, Lyon MF. X-chromosome inactivation in extra-embryonic membranes of diploid parthenogenetic mouse embryos demonstrated by differential staining. Nature. 1980;288:172–173. - PubMed
-
- McMahon A, Fosten M, Monk M. Random X-chromosome inactivation in female primordial germ cells in the mouse. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1981;64:251–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

