Apolipoprotein E-polymorphism, frailty and mortality in older adults
- PMID: 18266965
- PMCID: PMC3828888
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00270.x
Apolipoprotein E-polymorphism, frailty and mortality in older adults
Abstract
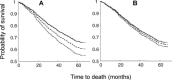
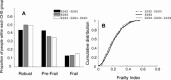
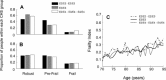
Although apolipoprotein E (ApoE) polymorphism is associated with variable risks of several illnesses, and with mortality, no persuasive relationship has been demonstrated with frailty. Here, the clinical examination cohort (n=1452 older adults, aged 70+ years at baseline) of the Canadian Study of Health and Aging was evaluated, with 5-year follow-up data. Frailty was defined using both the phenotypic definition from the Cardiovascular Health Study (Frailty-CHS) and the 'Frailty Index', from which age-specific trajectories of deficit accumulation can be estimated. In age-sex adjusted analyses, people with ApoE 4 allele had a higher risk of death (hazard ratio [HR]=1.20; 95% confidence interval: 1.01-1.45), but this relationship was not significant when adjusted for cognitive impairment (1.06; 95% confidence interval: 0.88-1.27). There was no association between frailty and ApoE polymorphism, defined in age-sex adjusted models either as Frailty-CHS (ApoE4 HR 1.17; 95% confidence interval: 0.98-1.40, frailty HR 1.37; 95% confidence interval: 1.28-1.46) or by the Frailty Index (ApoE4 HR 1.07; 95% confidence interval: 0.90-1.29, frailty HR 35.3; 95% confidence interval: 20.4-61.1). The data do not support an association between ApoE polymorphism and frailty. This result did not depend on how frailty was defined.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein E Polymorphism and Frailty: Apolipoprotein ε4 Allele Is Associated with Fatigue but Not Frailty Syndrome in a Community-Dwelling Older Population Cohort.J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25(4):410-415. doi: 10.1007/s12603-020-1522-1. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021. PMID: 33786555
-
Apolipoprotein E and Health in Older Men: The Concord Health and Ageing in Men Project.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020 Sep 25;75(10):1858-1862. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glaa105. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32342099
-
Prevalence and 10-year outcomes of frailty in older adults in relation to deficit accumulation.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010 Apr;58(4):681-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.02764.x. Epub 2010 Mar 22. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010. PMID: 20345864
-
Apolipoprotein E genotype determines survival in the oldest old (85 years or older) who have good cognition.Arch Neurol. 1996 May;53(5):418-22. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1996.00550050048022. Arch Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8624216
-
Apolipoprotein E polymorphism distribution in an elderly Brazilian population: the Bambuí Health and Aging Study.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007 Nov;40(11):1429-34. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2007001100002. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007. PMID: 17934638
Cited by
-
Apolipoprotein E-related all-cause mortality in hospitalized elderly patients.Age (Dordr). 2010 Sep;32(3):411-20. doi: 10.1007/s11357-010-9144-x. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Age (Dordr). 2010. PMID: 20640544 Free PMC article.
-
Differential moderation effects of ApoE and 5-HTTLPR genotypes on social vulnerability in predicting mortality among community-dwelling middle-aged and older adults: a nationwide population-based study.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Oct 14;13(19):23348-23360. doi: 10.18632/aging.203629. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34647905 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of smoking on the accumulation of deficits, frailty and survival in older adults: a secondary analysis from the Canadian Study of Health and Aging.J Nutr Health Aging. 2009 May;13(5):468-72. doi: 10.1007/s12603-009-0085-y. J Nutr Health Aging. 2009. PMID: 19390755
-
Age, gender, and cancer but not neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases strongly modulate systemic effect of the Apolipoprotein E4 allele on lifespan.PLoS Genet. 2014 Jan 30;10(1):e1004141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004141. eCollection 2014 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24497847 Free PMC article.
-
Vulnerability: the crossroads of frailty and delirium.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011 Nov;59 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S262-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03674.x. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011. PMID: 22091571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Song Y, Stampfer MJ, Liu S. Meta-analysis: apolipoprotein E genotypes and risk for coronary heart disease. Ann Intern Med. 2004;141:137–47. - PubMed
-
- Licastro F, Chiappelli M, Caldarera CM, Tampieri C, Nanni S, Gallina M, Branzi A. The concomitant presence of polymorphic alleles of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6 and apolipoprotein E is associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction in elderly men. Results from a pilot study. Mech Ageing Dev. 2004;5:575–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

