Acrolein: unwanted side product or contribution to antiangiogenic properties of metronomic cyclophosphamide therapy?
- PMID: 18266977
- PMCID: PMC3828885
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00255.x
Acrolein: unwanted side product or contribution to antiangiogenic properties of metronomic cyclophosphamide therapy?
Abstract
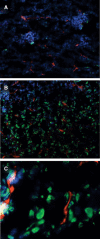
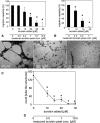
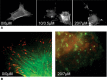
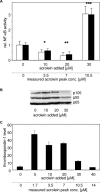
Tumour therapy with cyclophosphamide (CPA), an alkylating chemotherapeutic agent, has been associated with reduced tumour blood supply and antiangiogenic effects when applied in a continuous, low-dose metronomic schedule. Compared to conventional high-dose scheduling, metronomic CPA therapy exhibits antitumoural activity with reduced side effects. We have studied potential antiangiogenic properties of acrolein which is released from CPA after hydroxylation. Acrolein adducts were found in tumour cells and tumour endothelial cells of CPA-treated mice, suggesting an in vivo relevance of acrolein. In vitro, acrolein inhibited endothelial cell proliferation, endothelial cell migration and tube formation. Moreover, acrolein caused disassembly of the F-actin cytoskeleton and inhibition of alphavbeta3 integrin clustering at focal adhesions points in endothelial cells. Acrolein treatment modulated expression of thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1), an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis known to be linked to antiangiogenic effects of metronomic CPA therapy. Further on, acrolein treatment of primary endothelial cells modified NF-(kappa)B activity levels. This is the first study that points at an antiangiogenic activity of acrolein in metronomically scheduled CPA therapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improved antiangiogenic and antitumour activity of the combination of the natural flavonoid fisetin and cyclophosphamide in Lewis lung carcinoma-bearing mice.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;68(2):445-55. doi: 10.1007/s00280-010-1505-8. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21069336 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin 1, a mediator of the antiangiogenic effects of low-dose metronomic chemotherapy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12917-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2135406100. Epub 2003 Oct 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14561896 Free PMC article.
-
Collaboration between hepatic and intratumoral prodrug activation in a P450 prodrug-activation gene therapy model for cancer treatment.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Nov;6(11):2879-90. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0297. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17989319 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin-1 and pigment epithelium-derived factor enhance responsiveness of KM12 colon tumor to metronomic cyclophosphamide but have disparate effects on tumor metastasis.Cancer Lett. 2013 Apr 28;330(2):241-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.11.055. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23228633 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors: a mechanism of action of metronomic chemotherapy.Cancer Biol Ther. 2004 Dec;3(12):1212-3. doi: 10.4161/cbt.3.12.1369. Epub 2004 Dec 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15662130 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the carcinogenic potential of low-dose exposures to chemical mixtures in the environment: the challenge ahead.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S254-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv039. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26106142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transplant cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity: A comprehensive review.J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2024;16(4):211-221. doi: 10.34172/jcvtr.33230. Epub 2024 Dec 23. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2024. PMID: 40027370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acrolein induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and causes airspace enlargement.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e38038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038038. Epub 2012 May 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22675432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kozekov ID, Nechev LV, Moseley MS, Harris CM, Rizzo CJ, Stone MP, Harris TM. DNA interchain cross-links formed by acrolein and crotonaldehyde. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:50–61. - PubMed
-
- Wrabetz E, Peter G, Hohorst HJ. Does acrolein contribute to the cytotoxicity of cyclophosphamide? J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1980;98:119–26. - PubMed
-
- Munoz R, Shaked Y, Bertolini F, Emmenegger U, Man S, Kerbel RS. Anti-angiogenic treatment of breast cancer using metronomic low-dose chemotherapy. Breast. 2005;14:466–79. - PubMed
-
- Browder T, Butterfield CE, Kraling BM, Shi B, Marshall B, O'Reilly MS, Folkman J. Antiangiogenic scheduling of chemotherapy improves efficacy against experimental drug-resistant cancer. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1878–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

