Functional imaging: CT and MRI
- PMID: 18267192
- PMCID: PMC2435287
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccm.2007.12.003
Functional imaging: CT and MRI
Abstract
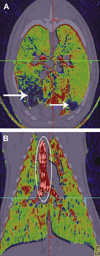
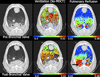
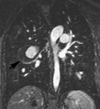
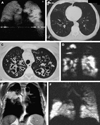
Numerous imaging techniques permit evaluation of regional pulmonary function. Contrast-enhanced CT methods now allow assessment of vasculature and lung perfusion. Techniques using spirometric controlled multi-detector row CT allow for quantification of presence and distribution of parenchymal and airway pathology; xenon gas can be employed to assess regional ventilation of the lungs, and rapid bolus injections of iodinated contrast agent can provide a quantitative measure of regional parenchymal perfusion. Advances in MRI of the lung include gadolinium-enhanced perfusion imaging and hyperpolarized gas imaging, which allow functional assessment, including ventilation/perfusion, microscopic air space measurements, and gas flow and transport dynamics.
Figures






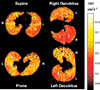
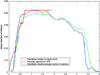
References
-
- Ritman EL, Robb RA, Harris LD. Imaging Physiological Functions: Experience with the DSR. Philadelphia: Praeger; 1985.
-
- Hoffman EA, Larsen RL. Regional Pulmonary Blood Flow via X-ray CT and Biodegradable Radiopaque Microspheres. Circulation. 1990;4:111–124.
-
- Boyd DP, Lipton MJ. Cardiac computed tomography; Proceedings of the IEEE; 1983. pp. 298–307.
-
- Saito T, Misaki M, Shirato K, Takishima T. Three-dimensional quantitative coronary angiography. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1990;37:768–777. - PubMed
-
- Saito Y. Multislice X-ray CT scanner. Medical Review. 1998 Nov;98:1–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

