On the nature of talker variability effects on recall of spoken word lists
- PMID: 1826729
- PMCID: PMC3507388
- DOI: 10.1037//0278-7393.17.1.152
On the nature of talker variability effects on recall of spoken word lists
Abstract
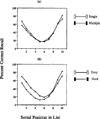
In a recent study, Martin, Mullennix, Pisoni, and Summers (1989) reported that subjects' accuracy in recalling lists of spoken words was better for words in early list positions when the words were spoken by a single talker than when they were spoken by multiple talkers. The present study was conducted to examine the nature of these effects in further detail. Accuracy of serial-ordered recall was examined for lists of words spoken by either a single talker or by multiple talkers. Half the lists contained easily recognizable words, and half contained more difficult words, according to a combined metric of word frequency, lexical neighborhood density, and neighborhood frequency. Rate of presentation was manipulated to assess the effects of both variables on rehearsal and perceptual encoding. A strong interaction was obtained between talker variability and rate of presentation. Recall of multiple-talker lists was affected much more than single-talker lists by changes in presentation rate. At slow presentation rates, words in early serial positions produced by multiple talkers were actually recalled more accurately than words produced by a single talker. No interaction was observed for word confusability and rate of presentation. The data provide support for the proposal that talker variability affects the accuracy of recall of spoken words not only by increasing the processing demands for early perceptual encoding of the words, but also by affecting the efficiency of the rehearsal process itself.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of talker variability on recall of spoken word lists.J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn. 1989 Jul;15(4):676-84. doi: 10.1037//0278-7393.15.4.676. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn. 1989. PMID: 2526857 Free PMC article.
-
Speech perception in children with cochlear implants: effects of lexical difficulty, talker variability, and word length.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 2000 Dec;185:79-81. doi: 10.1177/0003489400109s1234. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 2000. PMID: 11141016
-
Effects of stimulus variability on perception and representation of spoken words in memory.Percept Psychophys. 1995 Oct;57(7):989-1001. doi: 10.3758/bf03205458. Percept Psychophys. 1995. PMID: 8532502 Free PMC article.
-
Why are listeners hindered by talker variability?Psychon Bull Rev. 2024 Feb;31(1):104-121. doi: 10.3758/s13423-023-02355-6. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Psychon Bull Rev. 2024. PMID: 37580454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Give me enough time to rehearse: presentation rate modulates the production effect.Psychon Bull Rev. 2024 Aug;31(4):1603-1614. doi: 10.3758/s13423-023-02437-5. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Psychon Bull Rev. 2024. PMID: 38169042
Cited by
-
Vocal alignment to native and non-native speakers of English.J Acoust Soc Am. 2018 Aug;144(2):620. doi: 10.1121/1.5038567. J Acoust Soc Am. 2018. PMID: 30180696 Free PMC article.
-
Listening through voices: Infant statistical word segmentation across multiple speakers.Dev Psychol. 2015 Nov;51(11):1517-28. doi: 10.1037/a0039725. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Dev Psychol. 2015. PMID: 26389607 Free PMC article.
-
Eye movements reveal fast, voice-specific priming.J Exp Psychol Gen. 2016 Mar;145(3):314-37. doi: 10.1037/xge0000135. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Exp Psychol Gen. 2016. PMID: 26726911 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated software for analysis and synthesis of voice quality.Behav Res Methods. 2010 Nov;42(4):1030-41. doi: 10.3758/BRM.42.4.1030. Behav Res Methods. 2010. PMID: 21139170 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental trends in the interaction between auditory and linguistic processing.Percept Psychophys. 1993 Sep;54(3):310-20. doi: 10.3758/bf03205266. Percept Psychophys. 1993. PMID: 8414890
References
-
- Aldridge JW, Garcia HR, Mena G. Habitation as a necessary condition for maintenance rehearsal. Journal of Memory and Language. 1987;26:632–637.
-
- Allard F, Henderson L. Physical and name codes in auditory memory: The pursuit of an analogy. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology. 1976;28:475–482. - PubMed
-
- Baddeley AD, Hitch GJ. Working memory. In: Bower GH, editor. The psychology of learning and memory, vol. 8. New York: Academic; 1974. pp. 47–90.
-
- Cole RA, Coltheart M, Allard F. Memory of a speaker’s voice: Reaction time to same or different-voiced letters. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology. 1974;26:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Coltheart M, Davelaar E, Jonasson JT, Besner D. Access to the internal lexicon. In: Dornic S, editor. Attention and performance VI. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1977. pp. 535–555.

