IL-33 reduces the development of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 18268038
- PMCID: PMC2271006
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20071868
IL-33 reduces the development of atherosclerosis
Erratum in
- J Exp Med. 2012 Dec 17;209(13):2515
Abstract
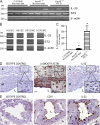
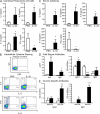
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the vasculature commonly leading to myocardial infarction and stroke. We show that IL-33, which is a novel IL-1-like cytokine that signals via ST2, can reduce atherosclerosis development in ApoE(-/-) mice on a high-fat diet. IL-33 and ST2 are present in the normal and atherosclerotic vasculature of mice and humans. Although control PBS-treated mice developed severe and inflamed atherosclerotic plaques in the aortic sinus, lesion development was profoundly reduced in IL-33-treated animals. IL-33 also markedly increased levels of IL-4, -5, and -13, but decreased levels of IFNgamma in serum and lymph node cells. IL-33 treatment also elevated levels of total serum IgA, IgE, and IgG(1), but decreased IgG(2a), which is consistent with a Th1-to-Th2 switch. IL-33-treated mice also produced significantly elevated antioxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) antibodies. Conversely, mice treated with soluble ST2, a decoy receptor that neutralizes IL-33, developed significantly larger atherosclerotic plaques in the aortic sinus of the ApoE(-/-) mice compared with control IgG-treated mice. Furthermore, coadministration of an anti-IL-5 mAb with IL-33 prevented the reduction in plaque size and reduced the amount of ox-LDL antibodies induced by IL-33. In conclusion, IL-33 may play a protective role in the development of atherosclerosis via the induction of IL-5 and ox-LDL antibodies.
Figures



References
-
- Hansson, G.K., and P. Libby. 2006. The immune response in atherosclerosis: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6:508–519. - PubMed
-
- Salonen, J.T., S. Yla-Herttuala, R. Yamamoto, S. Butler, H. Korpela, R. Salonen, K. Nyyssonen, W. Palinski, and J.L. Witztum. 1992. Autoantibody against oxidised LDL and progression of carotid atherosclerosis. Lancet. 339:883–887. - PubMed
-
- Major, A.S., S. Fazio, and M.F. Linton. 2002. B-lymphocyte deficiency increases atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-null mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 22:1892–1898. - PubMed
-
- de Boer, O.J., A.C. van der Wal, C.E. Verhagen, and A.E. Becker. 1999. Cytokine secretion profiles of cloned T cells from human aortic atherosclerotic plaques. J. Pathol. 188:174–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

