Brain redox imaging using blood-brain barrier-permeable nitroxide MRI contrast agent
- PMID: 18270519
- PMCID: PMC3197772
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2008.5
Brain redox imaging using blood-brain barrier-permeable nitroxide MRI contrast agent
Abstract
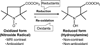
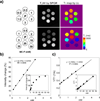
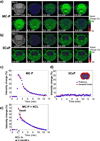
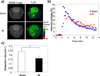
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and compromised antioxidant defense may contribute to brain disorders such as stroke, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, etc. Nitroxides are redox-sensitive paramagnetic contrast agents and antioxidants. The ability of a blood-brain barrier (BBB)-permeable nitroxide, methoxycarbonyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine-1-oxyl (MC-P), as a magnetic resonance-imaging (MRI) contrast agent for brain tissue redox imaging was tested. MC-P relaxation in rodent brain was quantified by MRI using a fast Look-Locker T(1)-mapping sequence. In the cerebral cortex and thalamus, the MRI signal intensity increased up to 50% after MC-P injection, but increased only by 2.7% when a BBB-impermeable nitroxide, 3CxP (3-carboxy-2,2,5,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine-1-oxyl) was used. The maximum concentrations in the thalamus and cerebral cortex after MC-P injection were calculated to be 1.9+/-0.35 and 3.0+/-0.50 mmol/L, respectively. These values were consistent with the ex vivo data of brain tissue and blood concentration obtained by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy. Also, reduction rates of MC-P were significantly decreased after reperfusion following transient MCAO (middle cerebral artery occlusion), a condition associated with changes in redox status resulting from oxidative damage. These results show the use of BBB-permeable nitroxides as MRI contrast agents and antioxidants to evaluate the role of ROS in neurologic diseases.
Figures
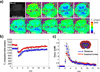
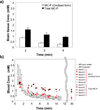
References
-
- Anzai K, Saito K, Takeshita K, Takahashi S, Miyazaki H, Shoji H, Lee MC, Masumizu T, Ozawa T. Assessment of ESR-CT imaging by comparison with autoradiography for the distribution of a blood-brain-barrier permeable spin probe, MC-PROXYL, to rodent brain. Magn Reson Imaging. 2003;21:765–772. - PubMed
-
- Anzai K, Ueno M, Yoshida A, Furuse M, Aung W, Nakanishi I, Moritake T, Takeshita K, Ikota N. Comparison of stable nitroxide, 3-substituted 2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine-N-oxyls, with respect to protection from radiation, prevention of DNA damage, and distribution in mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;40:1170–1178. - PubMed
-
- Chuang KH, Koretsky A. Improved neuronal tract tracing using manganese enhanced magnetic resonance imaging with fast T(1) mapping. Magn Reson Med. 2006;55:604–611. - PubMed
-
- Crawley AP, Henkelman RM. A comparison of one-shot and recovery methods in T1 imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1988;7:23–34. - PubMed
-
- Erker L, Schubert R, Yakushiji H, Barlow C, Larson D, Mitchell JB, Wynshaw-Boris A. Cancer chemoprevention by the antioxidant tempol acts partially via the p53 tumor suppressor. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14:1699–1708. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

