RNA-containing cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in ciliated bronchial epithelium months to years after acute Kawasaki disease
- PMID: 18270572
- PMCID: PMC2216059
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001582
RNA-containing cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in ciliated bronchial epithelium months to years after acute Kawasaki disease
Abstract
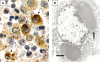
Background: Kawasaki Disease (KD) is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in children in developed nations. The KD etiologic agent is unknown but likely to be a ubiquitous microbe that usually causes asymptomatic childhood infection, resulting in KD only in genetically susceptible individuals. KD synthetic antibodies made from prevalent IgA gene sequences in KD arterial tissue detect intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies (ICI) resembling viral ICI in acute KD but not control infant ciliated bronchial epithelium. The prevalence of ICI in late-stage KD fatalities and in older individuals with non-KD illness should be low, unless persistent infection is common.
Methods and principal findings: Lung tissue from late-stage KD fatalities and non-infant controls was examined by light microscopy for the presence of ICI. Nucleic acid stains and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were performed on tissues that were strongly positive for ICI. ICI were present in ciliated bronchial epithelium in 6/7 (86%) late-stage KD fatalities and 7/27 (26%) controls ages 9-84 years (p = 0.01). Nucleic acid stains revealed RNA but not DNA within the ICI. ICI were also identified in lung macrophages in some KD cases. TEM of bronchial epithelium and macrophages from KD cases revealed finely granular homogeneous ICI.
Significance: These findings are consistent with a previously unidentified, ubiquitous RNA virus that forms ICI and can result in persistent infection in bronchial epithelium and macrophages as the etiologic agent of KD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Rowley AH, Shulman ST. Kawasaki Disease. In: Kliegman R, Behrman R, Jenson H, Stanton B, editors. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 18th edition. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2007. pp. 1036–42.
-
- Rowley AH, Shulman ST. New developments in the search for the etiologic agent of Kawasaki disease. Current Opinion in Pediatrics. 2007;19:71–74. - PubMed
-
- Rowley AH, Eckerley CA, Jack HM, Shulman ST, Baker SC. IgA plasma cells in vascular tissue of patients with Kawasaki syndrome. J Immunol. 1997;159:5946–55. - PubMed
-
- Rowley AH, Shulman ST, Mask CA, Finn LS, Terai M, et al. IgA plasma cell infiltration of proximal respiratory tract, pancreas, kidney, and coronary artery in acute Kawasaki disease. J Infect Dis. 2000;182:1183–91. - PubMed
-
- Rowley AH, Shulman ST, Spike BT, Mask CA, Baker SC. Oligoclonal IgA response in the vascular wall in acute Kawasaki disease. J Immunol. 2001;166:1334–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

