Breast tumor characteristics of BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutation carriers on MRI
- PMID: 18270717
- PMCID: PMC2292493
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-008-0851-y
Breast tumor characteristics of BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutation carriers on MRI
Abstract
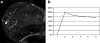
The appearance of malignant lesions in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers (BRCA-MCs) on mammography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was evaluated. Thus, 29 BRCA-MCs with breast cancer were retrospectively evaluated and the results compared with an age, tumor size and tumor type matched control group of 29 sporadic breast cancer cases. Detection rates on both modalities were evaluated. Tumors were analyzed on morphology, density (mammography), enhancement pattern and kinetics (MRI). Overall detection was significantly better with MRI than with mammography (55/58 vs 44/57, P=0.021). On mammography, lesions in the BRCA-MC group were significantly more described as rounded (12//19 vs 3/13, P=0.036) and with sharp margins (9/19 vs 1/13, P=0.024). On MRI lesions in the BRCA-MC group were significantly more described as rounded (16/27 vs 7/28, P=0.010), with sharp margins (20/27 vs 7/28, P<0.001) and with rim enhancement (7/27 vs 1/28, P=0.025). No significant difference was found for enhancement kinetics (P=0.667). Malignant lesions in BRCA-MC frequently have morphological characteristics commonly seen in benign lesions, like a rounded shape or sharp margins. This applies for both mammography and MRI. However the possibility of MRI to evaluate the enhancement pattern and kinetics enables the detection of characteristics suggestive for a malignancy.
Figures

References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1056/NEJM199705153362003', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199705153362003'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9145678', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9145678/'}]}
- Krainer M, Silva-Arrieta S, FitzGerald MG, Shimada A, Ishioka C, Kanamaru R, MacDonald DJ, Unsal H, Finkelstein DM, Bowcock A, Isselbacher KJ, Haber DA (1997) Differential contributions of BRCA1 and BRCA2 to early-onset breast cancer. N Engl J Med 336:1416–1421 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0140-6736(94)91578-4', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91578-4'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7907678', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7907678/'}]}
- Ford D, Easton DF, Bishop DT, Narod SA, Goldgar DE (1994) Risks of cancer in BRCA1-mutation carriers. Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Lancet 343:692–695 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1056/NEJM200107193450301', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200107193450301'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11463009', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11463009/'}]}
- Meijers-Heijboer H, van Geel B, van Putten WL, Henzen-Logmans SC, Seynaeve C, Menke-Pluymers MB, Bartels CC, Verhoog LC, van den Ouweland AM, Niermeijer MF, Brekelmans CT, Klijn JG (2001) Breast cancer after prophylactic bilateral mastectomy in women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation. N Engl J Med 345:159–164 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1056/NEJMoa020119', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa020119'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12023992', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12023992/'}]}
- Kauff ND, Satagopan JM, Robson ME, Scheuer L, Hensley M, Hudis CA, Ellis NA, Boyd J, Borgen PI, Barakat RR, Norton L, Castiel M, Nafa K, Offit K (2002) Risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy in women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation. N Engl J Med 346:1609–1615 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12342-2', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(03)12342-2'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12559863', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12559863/'}]}
- Cuzick J, Powles T, Veronesi U, Forbes J, Edwards R, Ashley S, Boyle P (2003) Overview of the main outcomes in breast-cancer prevention trials. Lancet 361: 296–300 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

