A collaborative epidemiological investigation into the criminal fake artesunate trade in South East Asia
- PMID: 18271620
- PMCID: PMC2235893
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050032
A collaborative epidemiological investigation into the criminal fake artesunate trade in South East Asia
Abstract
Background: Since 1998 the serious public health problem in South East Asia of counterfeit artesunate, containing no or subtherapeutic amounts of the active antimalarial ingredient, has led to deaths from untreated malaria, reduced confidence in this vital drug, large economic losses for the legitimate manufacturers, and concerns that artemisinin resistance might be engendered.
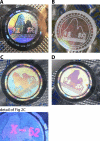
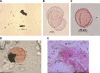
Methods and findings: With evidence of a deteriorating situation, a group of police, criminal analysts, chemists, palynologists, and health workers collaborated to determine the source of these counterfeits under the auspices of the International Criminal Police Organization (INTERPOL) and the Western Pacific World Health Organization Regional Office. A total of 391 samples of genuine and counterfeit artesunate collected in Vietnam (75), Cambodia (48), Lao PDR (115), Myanmar (Burma) (137) and the Thai/Myanmar border (16), were available for analysis. Sixteen different fake hologram types were identified. High-performance liquid chromatography and/or mass spectrometry confirmed that all specimens thought to be counterfeit (195/391, 49.9%) on the basis of packaging contained no or small quantities of artesunate (up to 12 mg per tablet as opposed to approximately 50 mg per genuine tablet). Chemical analysis demonstrated a wide diversity of wrong active ingredients, including banned pharmaceuticals, such as metamizole, and safrole, a carcinogen, and raw material for manufacture of methylenedioxymethamphetamine ('ecstasy'). Evidence from chemical, mineralogical, biological, and packaging analysis suggested that at least some of the counterfeits were manufactured in southeast People's Republic of China. This evidence prompted the Chinese Government to act quickly against the criminal traders with arrests and seizures.
Conclusions: An international multi-disciplinary group obtained evidence that some of the counterfeit artesunate was manufactured in China, and this prompted a criminal investigation. International cross-disciplinary collaborations may be appropriate in the investigation of other serious counterfeit medicine public health problems elsewhere, but strengthening of international collaborations and forensic and drug regulatory authority capacity will be required.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organisation. World Malaria Report – 2005. 2006. Available: http://www.rbm.who.int/wmr2005/html/1–2.htm. Accessed 22 July 2007.
-
- Anon. Malaria. World Health Organisation Media Centre. 2007. Available: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs094/en/index.html. Accessed 10 August 2007.
-
- Arrow KJ, Panosian CB, Gelband H. Saving lives, buying time: economics of malaria drugs in an age of resistance. Washington (DC): Institute of Medicine of the National Academies; 2004. Available: http://www.nap.edu/books/0309092183/html/. Accessed 5 August 2007. - PubMed
-
- Newton PN, Green MD, Fernández FM, Day NJP, White NJ. Counterfeit anti-infective medicines. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:602–613. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organisation. WHO guidelines for the treatment of malaria. Geneva: WHO; 2006. Available: www.who.int/malaria/docs/TreatmentGuidelines2006.pdf. Accessed 26 January 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

