Rats with chronic post-ischemia pain exhibit an analgesic sensitivity profile similar to human patients with complex regional pain syndrome--type I
- PMID: 18272148
- PMCID: PMC4492715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.01.006
Rats with chronic post-ischemia pain exhibit an analgesic sensitivity profile similar to human patients with complex regional pain syndrome--type I
Abstract
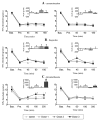
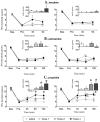
Chronic post-ischemia pain was induced in anesthetized rats by placing a tourniquet at the ankle joint for 3 h, and removing it to allow reperfusion. The effectiveness of standard analgesic drugs to attenuate mechanical allodynia was assessed 2 and 7 days after ischemia/reperfusion. Only high doses of morphine, dexamethasone and pregabalin partially reduced mechanical allodynia 2 days post-ischemia/reperfusion, while other treatments (ibuprofen, acetaminophen, amitriptyline) were not effective. Furthermore, only the highest dose of pregabalin reduced mechanical allodynia 7 days post-ischemia/reperfusion. These results are consistent with findings that complex region pain syndrome-I pain is refractory to most standard analgesic treatments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic post-ischemia pain (CPIP): a novel animal model of complex regional pain syndrome-type I (CRPS-I; reflex sympathetic dystrophy) produced by prolonged hindpaw ischemia and reperfusion in the rat.Pain. 2004 Nov;112(1-2):94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2004.08.001. Pain. 2004. PMID: 15494189
-
The efficacy of morphine, pregabalin, gabapentin, and duloxetine on mechanical allodynia is different from that on neuroma pain in the rat neuropathic pain model.Anesth Analg. 2012 Jul;115(1):182-8. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31824f94ca. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Anesth Analg. 2012. PMID: 22415534
-
Attenuation of neuropathy-induced allodynia following intraplantar injection of pregabalin.Can J Anaesth. 2010 Jul;57(7):664-71. doi: 10.1007/s12630-010-9318-0. Epub 2010 May 4. Can J Anaesth. 2010. PMID: 20440664
-
Gabapentin and pregabalin, but not morphine and amitriptyline, block both static and dynamic components of mechanical allodynia induced by streptozocin in the rat.Pain. 1999 Mar;80(1-2):391-8. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(98)00239-5. Pain. 1999. PMID: 10204753
-
Oxycodone combinations for pain relief.Drugs Today (Barc). 2010 Jun;46(6):379-98. doi: 10.1358/dot.2010.46.6.1470106. Drugs Today (Barc). 2010. PMID: 20571607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Topical combinations aimed at treating microvascular dysfunction reduce allodynia in rat models of CRPS-I and neuropathic pain.J Pain. 2013 Jan;14(1):66-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2012.10.004. J Pain. 2013. PMID: 23273834 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of peripheral blood flow in complex regional pain syndrome: clinical implication for symptomatic relief and pain management.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009 Sep 23;10:116. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-10-116. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009. PMID: 19775468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of NFkappaB in an animal model of complex regional pain syndrome-type I (CRPS-I).J Pain. 2009 Nov;10(11):1161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2009.04.012. J Pain. 2009. PMID: 19878863 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-allodynic Effect of Mangiferin in Rats With Chronic Post-ischemia Pain: A Model of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Oct 2;9:1119. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01119. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30333751 Free PMC article.
-
Manual Therapy Reduces Pain Behavior and Oxidative Stress in a Murine Model of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I.Brain Sci. 2019 Aug 10;9(8):197. doi: 10.3390/brainsci9080197. Brain Sci. 2019. PMID: 31405150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht PJ, Hines S, Eisenberg E, Pud D, Finlay DR, Connolly MK, Pare M, Davar G, Rice FL. Pathologic alterations of cutaneous innervation and vasculature in affected limbs from patients with complex regional pain syndrome. Pain. 2006;120:244–266. - PubMed
-
- Berthelot JM. Current management of reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome (complex regional pain syndrome type I) Joint Bone Spine. 2006;73:495–499. - PubMed
-
- Blaisdell FW. The pathophysiology of skeletal muscle ischemia and the reperfusion syndrome: a review. Cardiovasc Sur. 2002;10:620–630. - PubMed
-
- Bomholt SF, Mikkelsen JD, Blackburn-Munro G. Antinociceptive effects of the antidepressants amitriptyline, duloxetine, mirtazapine and citalopram in animal models of acute, persistent and neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology. 2005;48:252–263. - PubMed
-
- Caram-Salas NL, Medina-Santillan R, Reyes-Garcia G, Granados-Soto V. Antinociceptive synergy between dexamethasone and the B vitamin complex in a neuropathic pain model in the rat. Proc West Pharmacol Soc. 2004;47:88–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

