Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland: radiologic-pathologic correlation with MR imaging including diffusion-weighted imaging
- PMID: 18272554
- PMCID: PMC8128585
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A0974
Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland: radiologic-pathologic correlation with MR imaging including diffusion-weighted imaging
Abstract
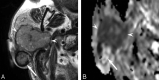
We present 4 cases of carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. In 3 of the 4 cases, diffusion-weighted and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) mapping images clearly revealed carcinoma as a hypercellular area with low ADC values and pleomorphic adenoma as a hypocellular area with high ADC values. Diffusion-weighted images demonstrated well complex tissue components in carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma, which may be useful for the diagnosis of this disease.
Figures

References
-
- Seifert G. Histopathology of malignant salivary gland tumours. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol 1992;28:49–56 - PubMed
-
- Olsen KD, Lewis JE. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma: a clinicopathologic review. Head Neck 2001;23:705–12 - PubMed
-
- Joe VQ, Westesson PL. Tumors of the parotid gland: MR imaging characteristics of various histologic types. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1994;163:433–38 - PubMed
-
- Freling NJ, Molenaar WM, Vermey A, et al. Malignant parotid tumors: clinical use of MR imaging and histologic correlation. Radiology 1992;185:691–96 - PubMed
-
- Motoori K, Yamamoto S, Ueda T, et al. Inter- and intratumoral variability in magnetic resonance imaging of pleomorphic adenoma: an attempt to interpret the variable magnetic resonance findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2004;28:233–46 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
