Contributions of inflammatory processes to the development of the early stages of diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 18274606
- PMCID: PMC2216058
- DOI: 10.1155/2007/95103
Contributions of inflammatory processes to the development of the early stages of diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
Diabetes causes metabolic and physiologic abnormalities in the retina, and these changes suggest a role for inflammation in the development of diabetic retinopathy. These changes include upregulation of iNOS, COX-2, ICAM-1, caspase 1, VEGF, and NF-kappaB, increased production of nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2, IL-1beta, and cytokines, as well as increased permeability and leukostasis. Using selective pharmacologic inhibitors or genetically modified animals, an increasing number of therapeutic approaches have been identified that significantly inhibit development of at least the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, especially occlusion and degeneration of retinal capillaries. A common feature of a number of these therapies is that they inhibit production of inflammatory mediators. The concept that localized inflammatory processes play a role in the development of diabetic retinopathy is relatively new, but evidence that supports the hypothesis is accumulating rapidly. This new hypothesis offers new insight into the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy, and offers novel targets to inhibit the ocular disease.
Figures


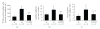
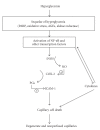
References
-
- Sima AA, Zhang W-X, Cherian PV, Chakrabarti S. Impaired visual evoked potential and primary axonopathy of the optic nerve in the diabetic BB/W-rat. Diabetologia. 1992;35(7):602–607. - PubMed
-
- Kamijo M, Cherian PV, Sima AAF. The preventive effect of aldose reductase inhibition on diabetic optic neuropathy in the BB/W-rat. Diabetologia. 1993;36(10):893–898. - PubMed
-
- Zeng X-X, Ng Y-K, Ling E-A. Neuronal and microglial response in the retina of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Visual Neuroscience. 2000;17(3):463–471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
