Positive impact of a shelter-based hepatitis B vaccine program in homeless Baltimore children and adolescents
- PMID: 18274908
- PMCID: PMC2430122
- DOI: 10.1007/s11524-008-9253-3
Positive impact of a shelter-based hepatitis B vaccine program in homeless Baltimore children and adolescents
Abstract
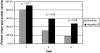
Homeless youth are at increased risk for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and HBV vaccine coverage is poor in this group. The purpose of our study was to determine if a shelter-based HBV vaccine program in children and adolescents 2-18 years of age with a randomized controlled trial using a culturally appropriate HBV video could increase HBV vaccine coverage rates. Subjects were randomized to an 8 min HBV video or a control, smoking prevention video. Before exposure to the videos, HBV knowledge, and demographics were assessed in caregivers and adolescents. HBV vaccine no. 1 was offered to all subjects who did not produce a vaccine record; subsequently, an accurate HBV vaccine history was obtained from medical providers. Subjects were asked to return 1 and 3 months after visit 1, HBV vaccine was offered to all with incomplete coverage, and HBV knowledge was reassessed. There were 328 children and adolescents cared for by 170 caregivers enrolled in the study. One hundred and four had incomplete HBV vaccine coverage. Data are reported for all family units with at least one subject needing vaccine. There were 53 children and adolescents randomized to the HBV video vs. 51 to the smoking video. HBV knowledge scores of caregivers improved at Visit no. 2 vs. no. 1 in the HBV video group (p = 0.01) but not in the smoking group (p = 0.82). Similar results were observed for adolescents in the HBV video group (p = 0.05) but not in the smoking group (p = 0.40). Exposure to the HBV video vs the smoking video had a significant effect on return rates for vaccine at Visit no. 2 (59 vs. 31%; p = 0.05) but not at Visit no. 3 (47 vs. 18%, p = 0.06). The shelter-based vaccine program was very effective in increasing HBV coverage rates in the entire group of 328 children and adolescents enrolled in the study, from 68% coverage at baseline to 85% at the conclusion of the study. We conclude that shelter-based HBV vaccine programs can be highly effective in increasing vaccine coverage rates in older children and adolescents. A brief exposure to a culturally appropriate HBV video improves HBV knowledge and may improve return rates for vaccine.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update recommendations to prevent hepatitis B virus transmission—United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1999;48:33–34. - PubMed
-
- Center for Diseases Control. Viral Hepatitis B: Frequently Asked Questions. Available at http://www/cdc/gov/ncidod/diseases/hepatitis/b/faqb.htm. Accessed on 12/8/2006.
-
- Schwarz K, Garrett B, Lamoreux J. Hepatitis B vaccination rate of homeless children in Baltimore. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006;41(2):225–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

